 司法数据公开
司法数据公开
Judicial Statistics- 商业纠纷案件立案情况
- Filing of Commercial Cases
- 商业纠纷案件结案情况
- Conclusion of Commercial Cases
- 商业纠纷案件执行情况
- Enforcement of Commercial Cases
- 商业纠纷案件调解情况
- Mediation of Commercial Cases
- 商业纠纷案件立案、审理、执行平均用时
- The Average Processing Time for Commercial Cases(Filing, Trial and Enforcement)
- 破产案件审理情况
- Trial of Insolvency Cases
- 不动产案件审理情况
- Trial of Real Property Cases
 司法文件公开
司法文件公开
Judicial Documents 裁判文书公开
裁判文书公开
Judgment Documents 庭审公开
庭审公开
Case Hearings > 诉讼服务公开
诉讼服务公开
Litigation Services> 典型案例公开
典型案例公开
Typical Cases 法官信息公开
Judge Informations>
法官信息公开
Judge Informations>
 立案情况
立案情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共受理一审、二审商业纠纷案件43076件,平均立案时间1.21天。
| 法院 | 商业纠纷案件立案数 | 平均立案天数/天 | 法院 | 商业纠纷案件立案数 | 平均立案天数/天 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商事/件 | 金融/件 | 不动产/件 | 商事/件 | 金融/件 | 不动产/件 | ||||
| 高院 | 7 | 79 | 3 | 0 | 静安 | 650 | 4570 | 425 | 0.86 |
| 一中 | 442 | 0 | 711 | 0.03 | 普陀 | 464 | 0 | 257 | 0.44 |
| 浦东 | 1561 | 7986 | 1403 | 1.34 | 宝山 | 1244 | 0 | 594 | 0.15 |
| 徐汇 | 811 | 0 | 417 | 3.21 | 嘉定 | 761 | 0 | 356 | 1.74 |
| 长宁 | 465 | 0 | 306 | 3.17 | 青浦 | 542 | 0 | 432 | 3.21 |
| 闵行 | 1151 | 0 | 808 | 1.2 | 崇明 | 181 | 0 | 175 | 1.09 |
| 金山 | 827 | 0 | 149 | 0.08 | 三中 | 119 | 0 | 5 | 1.61 |
| 松江 | 1108 | 0 | 454 | 1.63 | 知产 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 奉贤 | 687 | 0 | 226 | 0.31 | 海事 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 二中 | 745 | 0 | 670 | 0 | 金融 | 0 | 954 | 0 | 0 |
| 黄浦 | 390 | 6076 | 376 | 2.06 | 铁中 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 杨浦 | 512 | 0 | 318 | 0.4 | 沪铁 | 537 | 0 | 8 | 0.03 |
| 虹口 | 630 | 1236 | 248 | 0.05 | |||||
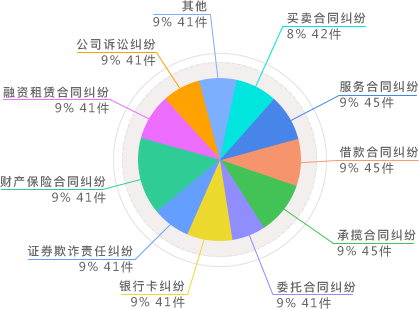
 案件类型
案件类型
 结案情况
结案情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共审结一审、二审商业纠纷案件 67779件,结案率为100%,审限内结案率为 99.91%,结收比157.35%。一审案件平均审理用时93.08天 ;二审案件平均审理用时64.8天 。
| 法院 | 商事/件 | 金融/件 | 不动产/件 | 结案率% | 审限内结案率% | 一审案件平均审理天数/天 | 二审案件平均审理天数/天 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高院 | 8 | 60 | 1 | 100 | 100 | - | 201.74 |
| 一中 | 527 | 0 | 821 | 100 | 100 | 239.22 | 67.35 |
| 浦东 | 2943 | 10668 | 3124 | 100 | 99.99 | 99.21 | - |
| 徐汇 | 953 | 0 | 627 | 100 | 100 | 101.38 | - |
| 长宁 | 673 | 0 | 424 | 100 | 100 | 185.36 | - |
| 闵行 | 1422 | 0 | 1119 | 100 | 99.96 | 128.39 | - |
| 金山 | 1503 | 0 | 498 | 100 | 99.85 | 97.53 | - |
| 松江 | 1728 | 0 | 764 | 100 | 99.88 | 81.7 | - |
| 奉贤 | 1601 | 0 | 390 | 100 | 100 | 108.44 | - |
| 二中 | 620 | 0 | 558 | 100 | 100 | 373.71 | 53.11 |
| 黄浦 | 441 | 8847 | 480 | 100 | 99.57 | 57.98 | - |
| 杨浦 | 847 | 0 | 386 | 100 | 100 | 108.19 | - |
| 虹口 | 783 | 1362 | 256 | 100 | 100 | 64.91 | - |
| 静安 | 1113 | 8855 | 580 | 100 | 99.96 | 59.2 | - |
| 普陀 | 1458 | 0 | 690 | 100 | 100 | 147.81 | - |
| 宝山 | 2006 | 0 | 685 | 100 | 100 | 95.3 | - |
| 嘉定 | 2049 | 0 | 756 | 100 | 100 | 136.22 | - |
| 青浦 | 1395 | 0 | 733 | 100 | 100 | 125.03 | - |
| 崇明 | 771 | 0 | 336 | 100 | 99.82 | 141.13 | - |
| 三中 | 135 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 98.52 | 163 | 113.67 |
| 知产 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 海事 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 金融 | 0 | 970 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 285.55 | 57.64 |
| 铁中 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 沪铁 | 798 | 0 | 15 | 100 | 100 | 124.11 | - |
 案件类型
案件类型
 执行情况
执行情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共办结执行案件21853件,未结24798件,执行案件执结率为100%,结收比为145.27%;各类案件平均执行用时94.92天,平均执行费用2570.78元。
| 法院 | 商业纠纷案件执行结案数 | 平均执行天数/天 | 平均执行费用/元 | 法院 | 商业纠纷案件执行结案数 | 平均执行天数/天 | 平均执行费用/元 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商事/件 | 金融/件 | 不动产/件 | 商事/件 | 金融/件 | 不动产/件 | ||||||
| 高院 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | - | 静安 | 296 | 824 | 133 | 76.02 | 594.57 |
| 一中 | 36 | 0 | 21 | 42.42 | 35479.6 | 普陀 | 442 | 6 | 174 | 143.55 | 498.1 |
| 浦东 | 1249 | 2340 | 1269 | 115.75 | 4855.16 | 宝山 | 879 | 10 | 271 | 119.19 | 596.4 |
| 徐汇 | 339 | 13 | 226 | 132.45 | 1907.9 | 嘉定 | 819 | 6 | 251 | 117.42 | 950.59 |
| 长宁 | 239 | 0 | 130 | 123.25 | 2853.21 | 青浦 | 487 | 9 | 176 | 129.76 | 1117.7 |
| 闵行 | 709 | 3 | 482 | 144.58 | 2785.04 | 崇明 | 331 | 0 | 571 | 99.95 | 1754.28 |
| 金山 | 586 | 4 | 121 | 95.03 | 1594.29 | 三中 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 118.57 | 2956.86 |
| 松江 | 655 | 6 | 600 | 99.4 | 1581.37 | 知产 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 奉贤 | 1006 | 12 | 190 | 93.73 | 4179.03 | 海事 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 二中 | 14 | 275 | 6 | 49.86 | - | 金融 | 0 | 61 | 0 | 266.07 | 46146.23 |
| 黄浦 | 150 | 3889 | 125 | 32.61 | 1497.1 | 铁中 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 杨浦 | 238 | 1 | 132 | 116.74 | 1158.16 | 沪铁 | 137 | 18 | 6 | 123.71 | 3779.39 |
| 虹口 | 188 | 534 | 143 | 58.59 | 1944.99 | ||||||
 案件类型
案件类型
 调解情况
调解情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院商业纠纷案件调解结案20349件。
| 法院 | 调解结案数/件 | 法院 | 调解结案数/件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高院 | 0 | 静安 | 4160 |
| 一中 | 3 | 普陀 | 553 |
| 浦东 | 3764 | 宝山 | 991 |
| 徐汇 | 567 | 嘉定 | 693 |
| 长宁 | 207 | 青浦 | 575 |
| 闵行 | 804 | 崇明 | 175 |
| 金山 | 545 | 三中 | 0 |
| 松江 | 770 | 知产 | 0 |
| 奉贤 | 440 | 海事 | 0 |
| 二中 | 0 | 金融 | 5 |
| 黄浦 | 4225 | 铁中 | 0 |
| 杨浦 | 319 | 沪铁 | 36 |
| 虹口 | 1517 |
说明:本图表统计的商业纠纷案件调解结案,包括先行调解成功案件,以及一审、二审民商事案件中以调解方式结案的案件。
 调解员情况
调解员情况
 破产案件总体情况
破产案件总体情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共受理各类破产案件602件,审结618件,平均审理用时352天。
适用三类破产程序具体情况
| 法院 | 破产清算 | 破产和解 | 破产重整 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结案数/件 | 平均审理天数/天 | 结案数/件 | 平均审理天数/天 | 结案数/件 | 平均审理天数/天 | |
| 浦东 | 120 | 390 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| 三中 | 494 | 336 | 0 | - | 3 | 1432 |
| 金融 | 1 | 350 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| 合计(/件)/平均(/天) | 615 | 358.67 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 477.33 |
 破产案件收、结数量变化情况
破产案件收、结数量变化情况
 不动产民事案件情况
不动产民事案件情况
不动产民事纠纷案件立案情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共受理一、二审不动产民事纠纷案件8341件,平均立案时间1.85天。
不动产民事纠纷案件结案情况
从2025年12月1日至2026年02月28日,上海法院共审结不动产民事纠纷案件13243件, 结案率为100%,结收比为158.77%,审限内结案率为99.98%。一审案件平均审理用时126.16天,二审案件平均审理用时59.87天。
 不动产行政纠纷情况
不动产行政纠纷情况
| 上海市不动产登记行政诉讼案件审理时限统计表 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年 度 | 纠纷总数(件) | 一审 | 二审 | 再审 | |||
| 一审数(件) | 平均审理用时(天) | 二审数(件) | 平均审理用时(天) | 再审数(件) | 平均审理用时(天) | ||
| 2017年 | 229 | 149 | 96.69 | 77 | 58.75 | 3 | 48 |
| 2018年 | 221 | 158 | 93.08 | 59 | 65.25 | 4 | 107.5 |
| 2019年 | 224 | 143 | 96.51 | 79 | 73.35 | 2 | 52.4 |
| 2020年 | 149 | 102 | 90.66 | 45 | 72.85 | 2 | 85 |
| 2021年 | 219 | 152 | 90.37 | 64 | 68.15 | 3 | 60.33 |
| 2022年 | 141 | 93 | 84.20 | 45 | 76.5 | 3 | 64 |
| 2023年 | 167 | 114 | 85.20 | 43 | 62.8 | 10 | 74.3 |
| 2024年 | 177 | 120 | 130.36 | 49 | 83 | 8 | 45.1 |
 Filing Cases
Filing Cases
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026, Shanghai Courts have accepted 43076 commercial cases of first and second instances, with the average time from filling to acceptance being 1.21 days.
| Court | Filling of cases | The average time from filling to acceptance | Court | Filling of cases | The average time from filling to acceptance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial | Financial | Real Property | Commercial | Financial | Real Property | ||||
| High | 7 | 79 | 3 | 0 | Jing’an | 650 | 4570 | 425 | 0.86 |
| First | 442 | 0 | 711 | 0.03 | Putuo | 464 | 0 | 257 | 0.44 |
| Pudong | 1561 | 7986 | 1403 | 1.34 | Baoshan | 1244 | 0 | 594 | 0.15 |
| Xuhui | 811 | 0 | 417 | 3.21 | Jiading | 761 | 0 | 356 | 1.74 |
| Changning | 465 | 0 | 306 | 3.17 | Qingpu | 542 | 0 | 432 | 3.21 |
| Minhang | 1151 | 0 | 808 | 1.2 | Chongming | 181 | 0 | 175 | 1.09 |
| Jinshan | 827 | 0 | 149 | 0.08 | Third | 119 | 0 | 5 | 1.61 |
| Songjiang | 1108 | 0 | 454 | 1.63 | Intellectual | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Fengxian | 687 | 0 | 226 | 0.31 | Maritime | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Second | 745 | 0 | 670 | 0 | Financial | 0 | 954 | 0 | 0 |
| Huangpu | 390 | 6076 | 376 | 2.06 | Tiezhong | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Yangpu | 512 | 0 | 318 | 0.4 | Hutie | 537 | 0 | 8 | 0.03 |
| Hongkou | 630 | 1236 | 248 | 0.05 | |||||
 Case type
Case type
 Conclusion Cases
Conclusion Cases
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026, Shanghai Courts have tried and concluded 67779 commercial cases of first and second instances,and the settlement rate is 100%.Among the concluded cases, 99.91% are dealt within the designated trial period,the closure-receipt ratio is 157.35%.The average trial period for first instance cases is 93.08 days; the average trial period for second instance cases is 64.8 days.
| Court | Commercial | Financial | Real Property | The settlement rate | The settlement rate within the designated trial period | The average trial period for first instance cases | The average trial period for second instance cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | 8 | 60 | 1 | 100 | 100 | - | 201.74 |
| First | 527 | 0 | 821 | 100 | 100 | 239.22 | 67.35 |
| Pudong | 2943 | 10668 | 3124 | 100 | 99.99 | 99.21 | - |
| Xuhui | 953 | 0 | 627 | 100 | 100 | 101.38 | - |
| Changning | 673 | 0 | 424 | 100 | 100 | 185.36 | - |
| Minhang | 1422 | 0 | 1119 | 100 | 99.96 | 128.39 | - |
| Jinshan | 1503 | 0 | 498 | 100 | 99.85 | 97.53 | - |
| Songjiang | 1728 | 0 | 764 | 100 | 99.88 | 81.7 | - |
| Fengxian | 1601 | 0 | 390 | 100 | 100 | 108.44 | - |
| Second | 620 | 0 | 558 | 100 | 100 | 373.71 | 53.11 |
| Huangpu | 441 | 8847 | 480 | 100 | 99.57 | 57.98 | - |
| Yangpu | 847 | 0 | 386 | 100 | 100 | 108.19 | - |
| Hongkou | 783 | 1362 | 256 | 100 | 100 | 64.91 | - |
| Jing’an | 1113 | 8855 | 580 | 100 | 99.96 | 59.2 | - |
| Putuo | 1458 | 0 | 690 | 100 | 100 | 147.81 | - |
| Baoshan | 2006 | 0 | 685 | 100 | 100 | 95.3 | - |
| Jiading | 2049 | 0 | 756 | 100 | 100 | 136.22 | - |
| Qingpu | 1395 | 0 | 733 | 100 | 100 | 125.03 | - |
| Chongming | 771 | 0 | 336 | 100 | 99.82 | 141.13 | - |
| Third | 135 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 98.52 | 163 | 113.67 |
| Financial | 0 | 970 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 285.55 | 57.64 |
| Hutie | 798 | 0 | 15 | 100 | 100 | 124.11 | - |
 Case type
Case type
 Enforcement Cases
Enforcement Cases
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026,Shanghai Courts have tried and concluded 21853 enforcement cases,and 24798 have not been concluded.The settlement rate of enforcement cases is 100%,the closure-receipt ratio is 145.27%.The average time for enforcement cases is 94.92 days,and the average cost for enforcement cases is ¥2570.78 .
| Court | Enforcement of Commercial Cases | The average time for enforcement | The average cost for enforcement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial | Financial | Real Property | |||
| High | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | - |
| First | 36 | 0 | 21 | 42.42 | 35479.6 |
| Pudong | 1249 | 2340 | 1269 | 115.75 | 4855.16 |
| Xuhui | 339 | 13 | 226 | 132.45 | 1907.9 |
| Changning | 239 | 0 | 130 | 123.25 | 2853.21 |
| Minhang | 709 | 3 | 482 | 144.58 | 2785.04 |
| Jinshan | 586 | 4 | 121 | 95.03 | 1594.29 |
| Songjiang | 655 | 6 | 600 | 99.4 | 1581.37 |
| Fengxian | 1006 | 12 | 190 | 93.73 | 4179.03 |
| Second | 14 | 275 | 6 | 49.86 | - |
| Huangpu | 150 | 3889 | 125 | 32.61 | 1497.1 |
| Yangpu | 238 | 1 | 132 | 116.74 | 1158.16 |
| Hongkou | 188 | 534 | 143 | 58.59 | 1944.99 |
| Jing’an | 296 | 824 | 133 | 76.02 | 594.57 |
| Putuo | 442 | 6 | 174 | 143.55 | 498.1 |
| Baoshan | 879 | 10 | 271 | 119.19 | 596.4 |
| Jiading | 819 | 6 | 251 | 117.42 | 950.59 |
| Qingpu | 487 | 9 | 176 | 129.76 | 1117.7 |
| Chongming | 331 | 0 | 571 | 99.95 | 1754.28 |
| Third | 7 | 7 | 0 | 118.57 | 2956.86 |
| Intellectual | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Maritime | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Financial | 0 | 61 | 0 | 266.07 | 46146.23 |
| Tiezhong | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Hutie | 137 | 18 | 6 | 123.71 | 3779.39 |
 Case type
Case type
 Mediation Cases
Mediation Cases
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026, Shanghai Courts have concluded 20349 commercial cases by mediation.
| Court | Mediation Cases | Court | Mediation Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | 0 | Jing’an | 4160 |
| First | 3 | Putuo | 553 |
| Pudong | 3764 | Baoshan | 991 |
| Xuhui | 567 | Jiading | 693 |
| Changning | 207 | Qingpu | 575 |
| Minhang | 804 | Chongming | 175 |
| Jinshan | 545 | Third | 0 |
| Songjiang | 770 | Intellectual | 0 |
| Fengxian | 440 | Maritime | 0 |
| Second | 0 | Financial | 5 |
| Huangpu | 4225 | Tiezhong | 0 |
| Yangpu | 319 | Hutie | 36 |
| Hongkou | 1517 |
Annotation: The statistics of commercial cases resolved by mediation in this sheet include:i)cases successfully concluded by pre-mediation, and ii) cases which have been settled by mediation in the trial process of first or second instances.
 Mediator
Mediator
 Trial of Insolvency Cases
Trial of Insolvency Cases
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026, Shanghai Courts have accepted 602 insolvency cases, among which 618 are tried and concluded. The average time for trial is 352 days.
※According to the Notice of the Shanghai High People’s Court on Adjusting the Centralized Jurisdiction of Compulsory Liquidation and Bankruptcy Cases of Shanghai Courts, since January 1st, 2022, insolvency cases within the jurisdiction of shanghai have been under the centralized jurisdiction of the Shanghai Third Intermediate People’s Court, the Shanghai Financial Court and the Shanghai Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court. Therefore, from January 1st,2022, only statistics for these three courts are presented.
Specific Status Applicable to the Three Types of Insolvency Procedures
| Court | Liquidation | Conciliation | Reorganization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conclusion | The average time for trial | Conclusion | The average time for trial | Conclusion | The average time for trial | |
| Pudong | 120 | 390 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Third | 494 | 336 | 0 | - | 3 | 1432 |
| Financial | 1 | 350 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Total(/piece)/Average(/day) | 615 | 358.67 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 477.33 |
 Changes in the number of insolvency cases accepted and concluded
Changes in the number of insolvency cases accepted and concluded
 Civil Cases of Real Property
Civil Cases of Real Property
Filing of Civil Cases of Real Property
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026,Shanghai Courts have accepted 8341 civil cases of Real Property, with the average time from filling to acceptance being 1.85 days.
Conclusion of Civil Cases of Real Property
From December 1, 2025 to February 28, 2026,Shanghai Courts have tried and concluded 13243 civil cases of Real Property, with the settlement rate of 100%. The rate of conclusion to filling is 158.77%. Among the concluded cases, 99.98% are dealt within the designated trial period.The average trial period for first instance cases is 126.16 days; the average trial period for second instance cases is 59.87 days.
 Administrative Disputes of Real Property
Administrative Disputes of Real Property
| Trial Period of Administrative Cases Involving Land Disputes in Shanghai | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Case | First Instance | Second Instance | Retrial | |||
| First Instance | The average trial period | Second Instance | The average trial period | Retrial | The average trial period | ||
| 2017 | 229 | 149 | 96.69 | 77 | 58.75 | 3 | 48 |
| 2018 | 221 | 158 | 93.08 | 59 | 65.25 | 4 | 107.5 |
| 2019 | 224 | 143 | 96.51 | 79 | 73.35 | 2 | 52.4 |
| 2020 | 149 | 102 | 90.66 | 45 | 72.85 | 2 | 85 |
| 2021 | 219 | 152 | 90.37 | 64 | 68.15 | 3 | 60.33 |
| 2022 | 141 | 93 | 84.20 | 45 | 76.5 | 3 | 64 |
| 2023 | 167 | 114 | 85.20 | 43 | 62.8 | 10 | 74.3 |
| 2024 | 177 | 120 | 130.36 | 49 | 83 | 8 | 45.1 |
 商业纠纷案件立案、审理、执行平均用时
商业纠纷案件立案、审理、执行平均用时
| 1.21 | + | 93.08 | + | 15 | + | 94.92 | = |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 立案 | 一审 | 上诉期 | 执行 |
总计
204.21天
| 1.21 | + | 93.08 | + | 15 | + | 64.8 | + | 94.92 | = |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 立案 | 一审 | 上诉期 | 二审 | 执行 |
总计
269.01天
“上诉用时”的统计方法:综合考量涉外与国内商业纠纷案件的上诉期不同,以及办案系统内相关数据统计可行性等因素,以统计期内上诉案件从一审法院移出至二审法院收案的平均用时为基础,在此基础上统一再增加30日,构成此处上海法院商业纠纷案件“上诉用时”。
 The Average Processing Time for Commercial Cases(Filing, Trial and Enforcement)
The Average Processing Time for Commercial Cases(Filing, Trial and Enforcement)
| 1.21 | + | 93.08 | + | 15 | + | 94.92 | = |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filling | First Instance | Appeal Period | Enforcement |
Total
204.21
| 1.21 | + | 93.08 | + | 15 | + | 64.8 | + | 94.92 | = |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filling | First Instance | Appeal Period | Second Instance | Enforcement |
Total
269.01
**Statistical method for “Appeal Time”: Taking into account factors such as the different appeal periods for foreign-related and domestic commercial disputes, as well as the feasibility of relevant data statistics in the case handling system, based on the average time it takes for cases to be transferred from the first instance court to the second instance court during the statistical period, an additional 30 days are uniformly added, so as to form the “appeal time” here for commercial dispute cases in Shanghai Courts.
最高人民法院关于全面深化人民法院改革的意见--人民法院第四个五年改革纲要(2014-2018)
法发〔2015〕3号
党的十八大从发展社会主义民主政治、加快建设社会主义法治国家的高度,作出了进一步深化司法体制改革的重要战略部署。党的十八届三中全会通过的《中共中央关于全面深化改革若干重大问题的决定》,确定了推进法治中国建设、深化司法体制改革的主要任务。党的十八届四中全会通过的《中共中央关于全面推进依法治国若干重大问题的决定》,将建设中国特色社会主义法治体系、建设社会主义法治国家作为全面推进依法治国的总目标,从科学立法、严格执法、公正司法、全民守法等方面提出了一系列重大改革举措。人民法院司法改革正面临前所未有的重大历史机遇。为贯彻党的十八大和十八届三中、四中全会精神,进一步深化人民法院各项改革,现制定《关于全面深化人民法院改革的意见》,并将之作为《人民法院第四个五年改革纲要(2014-2018)》贯彻实施。
一、全面深化人民法院改革的总体思路
全面深化人民法院改革的总体思路是:紧紧围绕让人民群众在每一个司法案件中感受到公平正义的目标,始终坚持司法为民、公正司法工作主线,着力解决影响司法公正、制约司法能力的深层次问题,确保人民法院依法独立公正行使审判权,不断提高司法公信力,促进国家治理体系和治理能力现代化,到2018年初步建成具有中国特色的社会主义审判权力运行体系,使之成为中国特色社会主义法治体系的重要组成部分,为实现“两个一百年”奋斗目标、实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦提供强有力的司法保障。
二、全面深化人民法院改革的基本原则
全面深化人民法院改革应当遵循以下基本原则:
--坚持党的领导,确保正确政治方向。人民法院深化司法改革,应当始终坚持党的领导,充分发挥党总揽全局、协调各方的领导核心作用,真正实现党的领导、人民当家作主、依法治国的有机统一,确保司法改革始终坚持正确的政治方向。
--尊重司法规律,体现司法权力属性。人民法院深化司法改革,应当严格遵循审判权作为判断权和裁量权的权力运行规律,彰显审判权的中央事权属性,突出审判在诉讼制度中的中心地位,使改革成果能够充分体现审判权的独立性、中立性、程序性和终局性特征。
--依法推动改革,确保改革稳妥有序。人民法院深化司法改革,应当坚持以宪法法律为依据,立足中国国情,依法有序推进,实现重大改革于法有据,推动将符合司法规律和公正司法要求的改革举措及时上升为法律。
--坚持整体推进,强调重点领域突破。人民法院深化司法改革,应当着力解决影响司法公正、制约司法能力的深层次问题,破解体制性、机制性、保障性障碍,同时要分清主次、突出重点,以问题为导向,确保改革整体推进。
--加强顶层设计,鼓励地方探索实践。人民法院深化司法改革,应当加强顶层设计,做好重大改革项目的统筹规划,注重改革措施的系统性、整体性和协同性,同时要尊重地方首创精神,鼓励下级法院在中央统一安排部署下先行先试,及时总结试点经验,推动制度创新。
三、全面深化人民法院改革的主要任务
(一)建立与行政区划适当分离的司法管辖制度
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须从维护国家法制统一、体现司法公正的要求出发,探索建立确保人民法院依法独立公正行使审判权的司法管辖制度。到2017年底,初步形成科学合理、衔接有序、确保公正的司法管辖制度。
1.设立最高人民法院巡回法庭。最高人民法院设立巡回法庭,审理跨行政区划的重大民商事、行政等案件,确保国家法律统一正确实施。调整跨行政区划重大民商事、行政案件的级别管辖制度,实现与最高人民法院案件管辖范围的有序衔接。
2.探索设立跨行政区划的法院。以科学、精简、高效和有利于实现司法公正为原则,探索设立跨行政区划法院,构建普通类型案件在行政区划法院受理、特殊类型案件在跨行政区划法院受理的诉讼格局。将铁路运输法院改造为跨行政区划法院,主要审理跨行政区划案件、重大行政案件、环境资源保护、企业破产、食品药品安全等易受地方因素影响的案件、跨行政区划人民检察院提起公诉的案件和原铁路运输法院受理的刑事、民事案件。
3.推动设立知识产权法院。根据知识产权案件的特点和审判需要,建立和完善符合知识产权案件审判规律的专门程序、管辖制度和审理规则。
4.改革行政案件管辖制度。通过提级管辖和指定管辖,逐步实现易受地方因素影响的行政案件由中级以上人民法院管辖。规范行政案件申请再审的条件和程序。
5.改革海事案件管辖制度。进一步理顺海事审判体制。科学确定海事法院管辖范围,建立更加符合海事案件审判规律的工作机制。
6.改革环境资源案件管辖制度。推动环境资源审判机构建设。进一步完善环境资源类案件的管辖制度。
7.健全公益诉讼管辖制度。探索建立与检察机关提起的公益诉讼相衔接的案件管辖制度。
8.继续推动法院管理体制改革。将林业法院、农垦法院统一纳入国家司法管理体系,理顺案件管辖机制,改革部门、企业管理法院的体制。
9.改革军事司法体制机制。完善统一领导的军事审判制度,维护国防利益,保障军人合法权益,依法打击违法犯罪。
(二)建立以审判为中心的诉讼制度
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须尊重司法规律,确保庭审在保护诉权、认定证据、查明事实、公正裁判中发挥决定性作用,实现诉讼证据质证在法庭、案件事实查明在法庭、诉辩意见发表在法庭、裁判理由形成在法庭。到2016年底,推动建立以审判为中心的诉讼制度,促使侦查、审查起诉活动始终围绕审判程序进行。
10.全面贯彻证据裁判原则。强化庭审中心意识,落实直接言词原则,严格落实证人、鉴定人出庭制度,发挥庭审对侦查、起诉程序的制约和引导作用。坚决贯彻疑罪从无原则,严格实行非法证据排除规则,进一步明确非法证据的范围和排除程序。
11.强化人权司法保障机制。彰显现代司法文明,禁止让刑事在押被告人或上诉人穿着识别服、马甲、囚服等具有监管机构标识的服装出庭受审。强化诉讼过程中当事人和其他诉讼参与人的知情权、陈述权、辩护辩论权、申请权、申诉权的制度保障。完善律师执业权利保障机制,强化控辩对等诉讼理念,禁止对律师进行歧视性安检,为律师依法履职提供便利。依法保障律师履行辩护代理职责,落实律师在庭审中发问、质证、辩论等诉讼权利。完善对限制人身自由司法措施和侦查手段的司法监督,加强对刑讯逼供和非法取证的源头预防,健全冤假错案的有效防范、及时纠正机制。
12.健全轻微刑事案件快速办理机制。在立法机关的授权和监督下,有序推进刑事案件速裁程序改革。
13.完善刑事诉讼中认罪认罚从宽制度。明确被告人自愿认罪、自愿接受处罚、积极退赃退赔案件的诉讼程序、处罚标准和处理方式,构建被告人认罪案件和不认罪案件的分流机制,优化配置司法资源。
14.完善民事诉讼证明规则。强化民事诉讼证明中当事人的主导地位,依法确定当事人证明责任。明确人民法院依职权调查收集证据的条件、范围和程序。严格落实证人、鉴定人出庭制度。发挥庭审质证、认证在认定案件事实中的核心作用。严格高度盖然性原则的适用标准,进一步明确法官行使自由裁量权的条件和范围。一切证据必须经过庭审质证后才能作为裁判的依据,当事人双方争议较大的重要证据都必须在裁判文书中阐明采纳与否的理由。
15.建立庭审全程录音录像机制。加强科技法庭建设,推动庭审全程同步录音录像。建立庭审录音录像的管理、使用、储存制度。规范以图文、视频等方式直播庭审的范围和程序。
16.规范处理涉案财物的司法程序。明确人民法院处理涉案财物的标准、范围和程序。进一步规范在刑事、民事和行政诉讼中查封、扣押、冻结和处理涉案财物的司法程序。推动建立涉案财物集中管理信息平台,完善涉案财物信息公开机制。
(三)优化人民法院内部职权配置
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须优化人民法院内部职权配置,健全立案、审判、执行、审判监督各环节之间的相互制约和相互衔接机制,充分发挥一审、二审和再审的不同职能,确保审级独立。到2016年底,形成定位科学、职能明确、运行有效的法院职权配置模式。
17.改革案件受理制度。变立案审查制为立案登记制,对人民法院依法应该受理的案件,做到有案必立、有诉必理,保障当事人诉权。加大立案信息的网上公开力度。推动完善诉讼收费制度。
18.完善分案制度。在加强专业化合议庭建设基础上,实行随机分案为主、指定分案为辅的案件分配制度。建立分案情况内部公示制度。对于变更审判组织或承办法官的,应当说明理由并公示。
19.完善审级制度。进一步改革民商事案件级别管辖制度,科学确定基层人民法院的案件管辖范围,逐步改变主要以诉讼标的额确定案件级别管辖的做法。完善提级管辖制度,明确一审案件管辖权从下级法院向上级法院转移的条件、范围和程序。推动实现一审重在解决事实认定和法律适用,二审重在解决事实和法律争议、实现二审终审,再审重在依法纠错、维护裁判权威。
20.强化审级监督。严格规范上级法院发回重审和指令再审的条件和次数,完善发回重审和指令再审文书的公开释明机制和案件信息反馈机制。人民法院办理二审、提审、申请再审及申诉案件,应当在裁判文书中指出一审或原审存在的问题,并阐明裁判理由。人民法院办理已经立案受理的申诉案件,应当向当事人出具法定形式的结案文书;符合公开条件的,一律在中国裁判文书网公布。
21.完善案件质量评估体系。建立科学合理的案件质量评估体系。废止违反司法规律的考评指标和措施,取消任何形式的排名排序做法。强化法定期限内立案和正常审限内结案,建立长期未结案通报机制,坚决停止人为控制收结案的错误做法。依托审判流程公开、裁判文书公开和执行信息公开三大平台,发挥案件质量评估体系对人民法院公正司法的服务、研判和导向作用。
22.深化司法统计改革。以“大数据、大格局、大服务”理念为指导,改革司法统计管理体制,打造分类科学、信息全面的司法统计标准体系,逐步构建符合审判实际和司法规律的实证分析模型,建立全国法院裁判文书库和全国法院司法信息大数据中心。
23.完善法律统一适用机制。完善最高人民法院的审判指导方式,加强司法解释等审判指导方式的规范性、及时性、针对性和有效性。改革和完善指导性案例的筛选、评估和发布机制。健全完善确保人民法院统一适用法律的工作机制。
24.深化执行体制改革。推动实行审判权和执行权相分离的体制改革试点。建立失信被执行人信用监督、威慑和惩戒法律制度。加大司法拍卖方式改革力度,重点推行网络司法拍卖模式。完善财产刑执行制度,推动将财产刑执行纳入统一的刑罚执行体制。
25.推动完善司法救助制度。明确司法救助的条件、标准和范围,规范司法救助的受理、审查和决定程序,严格资金的管理使用。推动国家司法救助立法,切实发挥司法救助在帮扶群众、化解矛盾中的积极作用。
26.深化司法领域区际国际合作。推动完善司法协助体制,扩大区际、国际司法协助覆盖面。推动制定刑事司法协助法。
(四)健全审判权力运行机制
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须严格遵循司法规律,完善以审判权为核心、以审判监督权和审判管理权为保障的审判权力运行机制,落实审判责任制,做到让审理者裁判,由裁判者负责。到2015年底,健全完善权责明晰、权责统一、监督有序、配套齐全的审判权力运行机制。
27.健全主审法官、合议庭办案机制。选拔政治素质好、办案能力强、专业水平高、司法经验丰富的审判人员担任主审法官。独任制审判以主审法官为中心,配备必要数量的审判辅助人员。合议制审判由主审法官担任审判长。合议庭成员都是主审法官的,原则上由承办案件的主审法官担任审判长。完善院、庭长、审判委员会委员担任审判长参加合议庭审理案件的工作机制。改革完善合议庭工作机制,明确合议庭作为审判组织的职能范围,完善合议庭成员在交叉阅卷、庭审、合议等环节中的共同参与和制约监督机制。改革裁判文书签发机制。
28.完善主审法官、合议庭办案责任制。按照权责利相统一的原则,明确主审法官、合议庭及其成员的办案责任与免责条件,实现评价机制、问责机制、惩戒机制、退出机制与保障机制的有效衔接。主审法官作为审判长参与合议时,与其他合议庭成员权力平等,但负有主持庭审活动、控制审判流程、组织案件合议、避免程序瑕疵等岗位责任。科学界定合议庭成员的责任,既要确保其独立发表意见,也要明确其个人意见、履职行为在案件处理结果中的责任。
29.健全院、庭长审判管理机制。明确院、庭长与其职务相适应的审判管理职责。规范案件审理程序变更、审限变更的审查报批制度。健全诉讼卷宗分类归档、网上办案、审判流程管控、裁判文书上网工作的内部督导机制。
30.健全院、庭长审判监督机制。明确院、庭长与其职务相适应的审判监督职责,健全内部制约监督机制。完善主审法官会议、专业法官会议机制。规范院、庭长对重大、疑难、复杂案件的监督机制,建立院、庭长在监督活动中形成的全部文书入卷存档制度。依托现代信息化手段,建立主审法官、合议庭行使审判权与院、庭长行使监督权的全程留痕、相互监督、相互制约机制,确保监督不缺位、监督不越位、监督必留痕、失职必担责。
31.健全审判管理制度。发挥审判管理在提升审判质效、规范司法行为、严格诉讼程序、统一裁判尺度等方面的保障、促进和服务作用,强化审判流程节点管控,进一步改善案件质量评估工作。
32.改革审判委员会工作机制。合理定位审判委员会职能,强化审判委员会总结审判经验、讨论决定审判工作重大事项的宏观指导职能。建立审判委员会讨论事项的先行过滤机制,规范审判委员会讨论案件的范围。除法律规定的情形和涉及国家外交、安全和社会稳定的重大复杂案件外,审判委员会主要讨论案件的法律适用问题。完善审判委员会议事规则,建立审判委员会会议材料、会议记录的签名确认制度。建立审判委员会决议事项的督办、回复和公示制度。建立审判委员会委员履职考评和内部公示机制。
33.推动人民陪审员制度改革。落实人民陪审员“倍增计划”,拓宽人民陪审员选任渠道和范围,保障人民群众参与司法,确保基层群众所占比例不低于新增人民陪审员三分之二。进一步规范人民陪审员的选任条件,改革选任方式,完善退出机制。明确人民陪审员参审案件职权,完善随机抽取机制。改革陪审方式,逐步实行人民陪审员不再审理法律适用问题,只参与审理事实认定问题。加强人民陪审员依法履职的经费保障。建立人民陪审员动态管理机制。
34.推动裁判文书说理改革。根据不同审级和案件类型,实现裁判文书的繁简分流。加强对当事人争议较大、法律关系复杂、社会关注度较高的一审案件,以及所有的二审案件、再审案件、审判委员会讨论决定案件裁判文书的说理性。对事实清楚、权利义务关系明确、当事人争议不大的一审民商事案件和事实清楚、证据确实充分、被告人认罪的一审轻微刑事案件,使用简化的裁判文书,通过填充要素、简化格式,提高裁判效率。重视律师辩护代理意见,对于律师依法提出的辩护代理意见未予采纳的,应当在裁判文书中说明理由。完善裁判文书说理的刚性约束机制和激励机制,建立裁判文书说理的评价体系,将裁判文书的说理水平作为法官业绩评价和晋级、选升的重要因素。
35.完善司法廉政监督机制。改进和加强司法巡查、审务督察和廉政监察员工作。建立上级纪委和上级法院为主、下级法院协同配合的违纪案件查处机制,实现纪检监察程序与法官惩戒程序的有序衔接。建立法院内部人员过问案件的记录制度和责任追究制度。依法规范法院人员与当事人、律师、特殊关系人、中介组织的接触、交往行为。
36.改革涉诉信访制度。完善诉访分离工作机制,明确诉访分离的标准、范围和程序。健全涉诉信访终结机制,依法规范涉诉信访秩序。建立就地接访督导机制,创新网络办理信访机制。推动建立申诉案件律师代理制度。探索建立社会第三方参与机制,增强涉诉信访矛盾多元化解合力。
(五)构建开放、动态、透明、便民的阳光司法机制
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须依托现代信息技术,构建开放、动态、透明、便民的阳光司法机制,增进公众对司法的了解、信赖和监督。到2015年底,形成体系完备、信息齐全、使用便捷的人民法院审判流程公开、裁判文书公开和执行信息公开三大平台,建立覆盖全面、系统科学、便民利民的司法为民机制。
37.完善庭审公开制度。建立庭审公告和旁听席位信息的公示与预约制度。对于依法应当公开审理,且受社会关注的案件,人民法院应当在已有条件范围内,优先安排与申请旁听者数量相适应的法庭开庭。有条件的审判法庭应当设立媒体旁听席,优先满足新闻媒体的旁听需要。
38.完善审判流程公开平台。推动全国法院政务网站建设。建立全国法院统一的诉讼公告网上办理平台和诉讼公告网站。继续加强中国审判流程信息公开网网站建设,完善审判信息数据及时汇总和即时更新机制。加快建设诉讼档案电子化工程。推动实现全国法院在同一平台公开审判流程信息,方便当事人自案件受理之日起,在线获取审判流程节点信息。
39.完善裁判文书公开平台。加强中国裁判文书网网站建设,完善其查询检索、信息聚合功能,方便公众有效获取、查阅、复制裁判文书。严格按照“以公开为原则,不公开为例外”的要求,实现四级人民法院依法应当公开的生效裁判文书统一在中国裁判文书网公布。
40.完善执行信息公开平台。整合各类执行信息,推动实现全国法院在同一平台统一公开执行信息,方便当事人在线了解执行工作进展。加强失信被执行人名单信息公布力度,充分发挥其信用惩戒作用,促使被执行人自动履行生效法律文书。完善被执行人信息公开系统建设,方便公众了解执行工作,主动接受社会监督。
41.完善减刑、假释、暂予监外执行公开制度。完善减刑、假释、暂予监外执行的适用条件和案件办理程序,确保相关案件公开、公正处理。会同刑罚执行机关、检察机关推动网上协同办案平台建设,对执法办案和考核奖惩中的重要事项、重点环节,实行网上录入、信息共享、全程留痕,从制度和技术上确保监督到位。建立减刑、假释、暂予监外执行信息网,实现三类案件的立案公示、庭审公告、文书公布统一在网上公开。
42.建立司法公开督导制度。强化公众对司法公开工作的监督,健全对违反司法公开规定行为的投诉机制和救济渠道。充分发挥司法公开三大平台的监督功能,使公众通过平台提出的意见和建议成为人民法院审判管理、审判监督和改进工作的重要参考依据。
43.完善诉讼服务中心制度。加强诉讼服务中心规范化建设,完善诉讼服务大厅、网上诉讼服务平台、12368司法服务热线。建立网上预约立案、送达、公告、申诉等工作机制。推动远程调解、信访等视频应用,进一步拓展司法为民的广度和深度。
44.完善人民法庭制度。优化人民法庭的区域布局和人员比例。积极推进以中心法庭为主、社区法庭和巡回审判点为辅的法庭布局形式。根据辖区实际情况,完善人民法庭便民立案机制。优化人民法庭人员构成。有序推进人民法庭之间、人民法庭和基层人民法院其他庭室之间的人员交流。
45.推动送达制度改革。推动建立当事人确认送达地址并承担相应法律后果的约束机制,探索推广信息化条件下的电子送达方式,提高送达效率。
46.健全多元化纠纷解决机制。继续推进调解、仲裁、行政裁决、行政复议等纠纷解决机制与诉讼的有机衔接、相互协调,引导当事人选择适当的纠纷解决方式。推动在征地拆迁、环境保护、劳动保障、医疗卫生、交通事故、物业管理、保险纠纷等领域加强行业性、专业性纠纷解决组织建设,推动仲裁制度和行政裁决制度的完善。建立人民调解、行政调解、行业调解、商事调解、司法调解联动工作体系。推动多元化纠纷解决机制立法进程,构建系统、科学的多元化纠纷解决体系。
47.推动实行普法责任制。强化法院普法意识,充分发挥庭审公开、文书说理、案例发布的普法功能,推动人民法院行使审判职能与履行普法责任的高度统一。
(六)推进法院人员的正规化、专业化、职业化建设
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须坚持以审判为中心、以法官为重心,全面推进法院人员的正规化、专业化、职业化建设,努力提升职业素养和专业水平。到2017年底,初步建立分类科学、分工明确、结构合理和符合司法职业特点的法院人员管理制度。
48.推动法院人员分类管理制度改革。建立符合职业特点的法官单独职务序列。健全法官助理、书记员、执行员等审判辅助人员管理制度。科学确定法官与审判辅助人员的数量比例,建立审判辅助人员的正常增补机制,切实减轻法官事务性工作负担。拓宽审判辅助人员的来源渠道,探索以购买社会化服务的方式,优化审判辅助人员结构。探索推动司法警察管理体制改革。完善司法行政人员管理制度。
49.建立法官员额制度。根据法院辖区经济社会发展状况、人口数量(含暂住人口)、案件数量、案件类型等基础数据,结合法院审级职能、法官工作量、审判辅助人员配置、办案保障条件等因素,科学确定四级法院的法官员额。根据案件数量、人员结构的变化情况,完善法官员额的动态调节机制。科学设置法官员额制改革过渡方案,综合考虑审判业绩、业务能力、理论水平和法律工作经历等因素,确保优秀法官留在审判一线。
50.改革法官选任制度。针对不同层级的法院,设置不同的法官任职条件。在国家和省一级分别设立由法官代表和社会有关人员参与的法官遴选委员会,制定公开、公平、公正的选任程序,确保品行端正、经验丰富、专业水平较高的优秀法律人才成为法官人选,实现法官遴选机制与法定任免机制的有效衔接。健全初任法官由高级人民法院统一招录,一律在基层人民法院任职机制。配合法律职业人员统一职前培训制度改革,健全预备法官训练制度。适当提高初任法官的任职年龄。建立上级法院法官原则上从下一级法院遴选产生的工作机制。完善将优秀律师、法律学者,以及在立法、检察、执法等部门任职的专业法律人才选任为法官的制度。健全法院和法学院校、法学研究机构人员双向交流机制,实施高校和法院人员互聘计划。
51.完善法官业绩评价体系。建立科学合理、客观公正、符合规律的法官业绩评价机制,完善评价标准,将评价结果作为法官等级晋升、择优遴选的重要依据。建立不适任法官的退出机制,完善相关配套措施。
52.完善法官在职培训机制。严格以实际需求为导向,坚持分类、分级、全员培训,着力提升法官的庭审驾驭能力、法律适用能力和裁判文书写作能力。改进法官教育培训的计划生成、组织调训、跟踪管理和质量评估机制,健全教学师资库、案例库、精品课件库。加强法官培训机构和现场教学基地建设。建立中国法官教育培训网,依托信息化手段,大力推广网络教学,实现精品教学课件由法院人员免费在线共享。大力加强基层人民法院法官和少数民族双语法官的培训工作。
53.完善法官工资制度。落实法官法规定,研究建立与法官单独职务序列配套的工资制度。
(七)确保人民法院依法独立公正行使审判权
建立中国特色社会主义审判权力运行体系,必须坚持在党的领导下,推动完善确保人民法院依法独立公正行使审判权的各项制度,优化司法环境,树立司法权威,强化职业保障,提高司法公信力。到2018年底,推动形成信赖司法、尊重司法、支持司法的制度环境和社会氛围。
54.推动省级以下法院人员统一管理改革。配合中央有关部门,推动建立省级以下地方法院人员编制统一管理制度。推动建立省级以下地方法院法官统一由省级提名、管理并按法定程序任免的机制。
55.建立防止干预司法活动的工作机制。配合中央有关部门,推动建立领导干部干预审判执行活动、插手具体案件处理的记录、通报和责任追究制度。按照案件全程留痕要求,明确审判组织的记录义务和责任,对于领导干部干预司法活动、插手具体案件的批示、函文、记录等信息,建立依法提取、介质存储、专库录入、入卷存查机制,相关信息均应当存入案件正卷,供当事人及其代理人查询。
56.健全法官履行法定职责保护机制。合理确定法官、审判辅助人员的工作职责、工作流程和工作标准。明确不同主体、不同类型过错的甄别标准和免责事由,确保法官依法履职行为不受追究。非因法定事由,未经法定程序,不得将法官调离、辞退或者作出免职、降级等处分。完善法官申诉控告制度,建立法官合法权益因依法履职受到侵害的救济机制,健全不实举报澄清机制。在国家和省一级分别设立由法官代表和社会有关人员参与的法官惩戒委员会,制定公开、公正的法官惩戒程序,既确保法官的违纪违法行为及时得到应有惩戒,又保障其辩解、举证、申请复议和申诉的权利。
57.完善司法权威保障机制。推动完善拒不执行判决、裁定、藐视法庭权威等犯罪行为的追诉机制。推动相关法律修改,依法惩治当庭损毁证据材料、庭审记录、法律文书和法庭设施等严重藐视法庭权威的行为,以及在法庭之外威胁、侮辱、跟踪、骚扰法院人员或其近亲属等违法犯罪行为。
58.强化诉讼诚信保障机制。建立诉讼诚信记录和惩戒制度。依法惩治虚假诉讼、恶意诉讼、无理缠诉行为,将上述三类行为信息纳入社会征信系统。探索建立虚假诉讼、恶意诉讼受害人损害赔偿之诉。
59.优化行政审判外部环境。健全行政机关负责人依法出庭应诉制度,引导、规范行政机关参加诉讼活动。规范司法建议的制作和发送,促进依法行政水平提升。
60.完善法官宣誓制度。完善法官宣誓制度,经各级人大及其常委会选举或任命的法官,正式就职时应当公开向宪法宣誓。
61.完善司法荣誉制度。明确授予法官、审判辅助人员不同类别荣誉的标准、条件和程序,提升法院人员的司法职业尊荣感和归属感。
62.理顺法院司法行政事务管理关系。科学设置人民法院的司法行政事务管理机构,规范和统一管理职责,探索实行法院司法行政事务管理权和审判权的相对分离。改进上下级法院司法行政事务管理机制,明确上级法院司法行政事务管理部门对下级法院司法行政事务的监管职能。
63.推动人民法院财物管理体制改革。配合中央有关部门,推动省级以下地方法院经费统一管理机制改革。完善人民法院预算保障体系、国库收付体系和财务管理体系,推动人民法院经费管理与保障的长效机制建设。严格“收支两条线”管理,地方各级人民法院收取的诉讼费、罚金、没收的财物,以及追缴的赃款赃物等,统一上缴省级国库。加强“两庭”等场所建设。建立人民法院装备标准体系。
64.推动人民法院内设机构改革。按照科学、精简、高效的工作要求,推进扁平化管理,逐步建立以服务审判工作为重心的法院内设机构设置模式。
65.推动人民法院信息化建设。加快“天平工程”建设,着力整合现有资源,推动以服务法院工作和公众需求的各类信息化应用。最高人民法院和高级人民法院主要业务信息化覆盖率达到100%,中级人民法院和基层人民法院分别达到95%和85%以上。
四、全面深化人民法院改革的工作要求
全面深化人民法院改革,任务艰巨、责任重大、时间紧迫。各级人民法院要认真贯彻中央决策部署,加强组织领导,完善工作机制,有重点、有步骤、有秩序地抓好落实和推动工作,确保改革措施取得实际效果,改革成果惠及全体人民。
最高人民法院司法改革领导小组是人民法院司法改革的议事、协调和指导机构,不定期召开小组会议,研究确定改革要点、审议改革方案、听取进度汇报、讨论决定重大问题。
最高人民法院建立情况通报、督导检查、评估总结制度,及时掌握改革动态,加强督促指导,纠正错误做法,总结成功经验,做到每项改革任务都有布置、有督促、有检查,确保各项任务不折不扣完成。
各高级人民法院应当成立司法改革领导小组,监督指导、统筹协调辖区内法院的司法改革工作。各级人民法院要建立健全司法改革事务报批备案和请示报告制度,及时总结改革经验、报告工作进展、反映问题困难。各高级人民法院拟就部分改革项目开展试点的,试点方案须报最高人民法院审批同意,重大改革试点方案须经最高人民法院报中央审批同意方可实施。
最高人民法院
2015年2月4日
Opinions of the Supreme People’s Court on Deepening the Reform of People's Courts in All Respects - the Fourth Five-Year Reform Plan of the People's Courts (2014-2018)
No. 3 [2015] of the Supreme People’s Court
The 18th CPC National Congress has made important strategic arrangements for further deepening the reform of the judicial system from the new level of developing socialist democracy and accelerating the establishment of a socialist country under the rule of law. The Decision of the CCCPC on Some Major Issues Concerning Comprehensively Deepening the Reform adopted at the Third Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee has determined the main tasks of advancing the construction of the rule of law in China and deepening the reform of the judicial system. The Decision of the CPC Central Committee on Several Important Issues of Comprehensively Advancing Rule of Law adopted at the Fourth Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee has set the establishment of
I. General Guideline on Comprehensive Deepening of Reform of People's Courts
The general guideline on comprehensive deepening of reform of People's Courts is: by sticking to the goal of making the people feel impartiality and justice in each and every judicial case and consistently adhering to the main line of judiciary for the people and the work of judicial fairness, to work hard to resolve the underlying issues affecting judicial fairness and restricting judicial capabilities, and ensure that people’s courts exercise their jurisdiction independently and impartially in accordance with the law, continuously improve the judicial credibility, and promote the modernization of the country's governance system and capabilities. By 2018, we will initially establish a socialist judiciary power operating system with Chinese characteristics, making it an important part of socialist rule of law system with Chinese characteristic, which provides a strong judicial guarantee for the realization of the "Two Centenary Goals" objective and the Chinese dream of realizing the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
II. Basic Principles Governing Comprehensive Deepening of Reform of People's Courts
To comprehensively deepen the reform of people’s courts shall be in compliance with the following basic principles:
-- Upholding the leadership of the Party and adhering to a correct political direction. Deepening of the judicial reform by people’s courts should always uphold the leadership of the Party, bring into full the role as the leadership core in exercising overall leadership and coordinating all efforts, truly achieve organic unity of leadership of the Party, ruling of the country by the people and the rule of law and ensure that judicial reform always adheres to the correct political direction.
-- Respecting the law of justice and reflecting the attributes of judicial power. To deepen judicial reforms, people's courts should strictly follow the law with which power operates that judicial power serves as the judging and discretionary power, highlight the attribute of central committee power or authority of the judicial power and emphasize the central position of trials in the litigation system so that the results of reforms can fully reflect the independence, neutrality, procedural and final attributes of the judicial power.
-- Promoting reform in accordance with the law and ensuring that the reform
-- Adhering to the overall advancement and emphasizing breakthroughs in key areas. To deepen judicial reform, people's courts should focus on solving the deep-seated issues affecting judicial fairness and restricting judicial capabilities, removing barriers on the part of systems, mechanisms and security. At the same time, people’ courts must distinguish between primary and secondary issues, stress the key point, be problem-oriented and ensure the overall advancement of reform.
-- Strengthening top-level design and encouraging local explorations and practices. To deepen judicial reform, people's courts should strengthen top-level design, make overall plans for major reform projects, and pay attention to the systematicness, integrity and synergy of reform measures. At the same time, people’s courts must respect local initiatives and encourage courts at lower levels to be the first to act and operate pilot projects under unified arrangement and planning by the Central Government,, sum up the pilot experience in a timely manner and promote institutional innovation.
III. Major
(I) Establishing a judicial jurisdiction system that is appropriately separated from administrative division
To establish the system of operation of socialist judicial power with Chinese characteristics, it is necessary to proceed from the requirements of safeguarding the unification of the country’s legal system and reflecting the fairness of the judiciary, and to explore and establish a judicial jurisdiction system that ensures that people’s courts independently and fairly exercise their judicial power according to law. By the end of 2017, a scientific and rational system of judicial jurisdiction with orderly coordination for ensuring impartiality shall have initially formed.
1. Setting up circuit courts of the Supreme People’s Court. The Supreme People's Court establishes circuit courts to hear major civil and commercial affairs and administrative cases across administrative divisions in order to ensure that national laws are uniformly and correctly implemented. The system of graded jurisdiction over major civil, commercial and administrative cases across different administrative divisions shall be adjusted, to realize orderly coordination with the scope of jurisdiction over cases by the Supreme People's Court.
2. Exploring the establishment of courts across different administrative divisions. Under the principle of scientificity, streamlining, high efficiency and benefiting realization of judicial impartiality, exploration shall be made for establishing courts across different administrative divisions, to develop a pattern of legal proceedings under which ordinary types of cases are acceptable for trial by courts within the relevant administrative divisions and special types of cases are acceptable for trial by courts across different administrative regions. All railway transportation courts shall be transformed into courts across different administrative divisions, which shall mainly try cases across different administrative divisions, major administrative cases, cases of environment and resources protection, enterprise bankruptcy, food and drug safety, etc that are vulnerable to influence of local factors, cases prosecuted by People's Procuratorates across different administrative divisions, and criminal and civil cases previously acceptable for trial by former railway transportation courts.
3. Promoting the establishment of an intellectual property courts. In accordance with the characteristics of intellectual property cases and the need for trials, exclusive procedures, systems of jurisdiction and rules for trial meeting the law of trial of intellectual property cases shall be established and perfected.
4. Reforming the administrative case jurisdiction system. By means of assigning jurisdiction to courts at higher levels and jurisdiction by designated courts, jurisdiction by intermediary courts and courts at higher levels over administrative cases that are vulnerable to influence of local factors shall be gradually realized. The conditions and procedures for application for retrial of administrative cases shall be standardized.
5. Reforming the maritime case jurisdiction system. The system of maritime justice shall be further rectified.The scope of jurisdiction of maritime courts shall be
6. Reforming the environmental resource case jurisdiction system. Construction of institutions for justice of the environment and resources shall be promoted. The system of jurisdiction over cases in the category of the environment and resources shall be further improved.
7. Improving the public interest litigation jurisdiction system. Exploration shall be made for establishing a system of jurisdiction over cases prosecuted by prosecutorial organs that is in coordination with public interest legal proceedings.
8. Continuing to promote the reform of the court management system. Forestry courts and land-reclamation and-cultivation court shall be brought under the coverage of the national justice management system on a unified basis, in rectification of the system of jurisdiction over cases, and in reform of the system of management of courts by departments and enterprises.
9. Reforming the military judicial system mechanism. The military adjudication system under unified leadership shall be improved, to maintain interests of national defense, to protect the legitimate rights and interests of servicemen, and to crack down on law violations and crimes in accordance with law.
(II) Establishing a trial-oriented litigation system
To establish the system of operation of socialist judicial power with Chinese characteristics, the law of justice must be respected to ensure the court hearing plays a decisive role in protecting the right to lodge complaints, identifying evidence, ascertaining facts, and impartial judgment, and
10. Fully implementing the principle of evidentiary adjudication. The awareness about court trial centralism shall be strengthened. The principle of direct wordage shall be implemented. The system of appearance of witnesses and appraisers in court shall be strictly implemented. The inhibitive and guiding effect of court trial to procedures for investigation and to institution of legal proceedings shall be brought into play. The principle of no punishment in doubtful cases shall be resolutely implemented. The illegal evidence removal rule shall be strictly applied. The scope of illegal evidence and the procedure for removal thereof shall be further defined.
11. Strengthening of mechanisms for judicial protection of human rights: The modern judicature civilization shall be demonstrated, with prohibition of appearance in court of criminal defendants in custody and criminal appellants wearing identification clothes, waistcoats, prison uniforms, etc with labels of regulators to receive trial. Systemic protection of the right to be informed, the right of statement, the right to defense, the right to debate, the right of application and the right of appeal on the part of the parties concerned and other legal proceedings participants in the legal process shall be strengthened. Mechanisms for protecting the rights of lawyers in the practice of law shall be improved, and the judicial concept of equality of the accusing party and the defense shall be strengthened, with prohibition of discriminative security check on lawyers, and with provision of convenience for lawyers to fulfill their duty in accordance with law. Fulfillment of the duty of defense and representation by lawyers shall be protected in accordance with law. The rights of action of lawyers including questioning, cross examination and debate in court trial shall be honored. Judicial supervision over judicial measures and means of investigation restricting personal freedom shall be improved. Prevention and control from the source of extortion of confession by torture and illegal collection of evidence shall be strengthened. Mechanisms for effective prevention and timely correction of cases of unjust, fake and false charges shall be made completed.
12. Perfection of mechanisms for rapid handling of minor criminal cases: Under authorization and supervision by legislative authorities, reform of the procedures for rapid ruling in criminal cases shall be promoted in an orderly manner.
13. Improvement of the system of leniency for acknowledgement of guilt and acceptance of punishment in criminal proceedings: The contentious procedures and punishment standards for and the mode of processing of cases in which defendants voluntarily acknowledge guilt, voluntarily accept punishment, and actively give up ill-gotten gains and pay compensation shall be defined; and mechanisms for diverting cases in which defendants plead guilty and cases in which defendants plead not guilty shall be established, to optimize the distribution of judicial resources.
14. Improving civil litigation certification rules. The leading status of the parties concerned in proof in civil litigation shall be strengthened, and the burden of proof by the parties concerned shall be determined in accordance with law. The conditions for, the scope of and the procedures for investigation and collection of evidence by People's Courts by virtue of their authority of office shall be defined. The system of appearance in court by witnesses and appraisers shall be strictly implemented. The core role of cross examination and attestation during court trial in determining facts in cases shall be brought into play. The standards for applying the principle of high probability shall be made strict, and the conditions for and the scope of exercise of the right of discretion by judges shall be further defined. Only after undergoing cross examination in court trial can all evidence be used as basis for ruling and judgment; and for important evidence which is relatively seriously controversial between the two parties concerned, the reason for whether to adopt it or not must be specified in documents of ruling or judgment.
15. Establishing a trial-process video and audio recording mechanism. The construction of scientific and technological courts shall be strengthened, and synchronous video and audio recording during the whole process of court trial shall be promoted. Systems of management, use and storage of video and audio recordings of court trial shall be established. The scope of and the procedures for live broadcast of court trials with photos and articles, video signals, etc shall be regulated.
16. Standardizing the judicial procedures for dealing with the property involved. Standardization of judicial procedures for disposing of property involved in cases: The standards for, the scope of and the procedures for disposal of property involved in cases by People's Courts shall be defined. Judicial procedures for sealing up, seizing, freezing and disposing of property involved in cases in criminal, civil and administrative proceedings shall be further standardized. Establishment of information platforms for centralized management of property involved in cases shall be promoted, and mechanisms for disclosure of information on property involved in cases shall be improved.
(III) Optimizing the allocation of the authority of office within
In the establishment of the system of operation of socialist judicial power with Chinese characteristics, distribution of the authority of office within People's Courts must be optimized; and mechanisms for mutual inhibition and mutual coordination among all links of case filing, trial, enforcement and trial supervision shall be made complete, with the different functions of trial of first instance, trial of second instance and retrial brought into full play, to ensure independence of trial grades. By the end of 2016, models for the distribution of the authority of office of courts with scientific definition, specific functions and effective operation shall have formed.
17. Reforming the case acceptance system. The case filing review system shall be changed for the case filing registration system; and for cases that shall be accepted by People's Courts for processing in accordance with law, they shall be filed as long as they are in existence, and the suits in them shall be processed as long as they are in existence, to protect the right of action of the parties concerned. Efforts for online disclosure of information on case filing shall be strengthened. Improvement of the litigation fee charge system shall be promoted.
18. Improving the case
19. Improving the level of trial system. The system of graded jurisdiction over civil and commercial cases shall be further reformed, with scientific determination of the scope of jurisdiction over cases by grassroots level People's Courts, and with gradual change of the approach of determining graded jurisdiction over cases mainly by the value of objects of action. The system of assigning jurisdiction to courts at higher levels shall be improved, with definition of the conditions for, the scope of and the procedures for transferring jurisdiction over cases of trial of first instance from courts at lower levels to courts at higher levels. Realization of focusing on settling determination of facts and application of law in trial of first instance and focusing on settling disputes over facts and law in trial of second instance to realize trial of second instance being trial of final instance, and realization of focusing on correction of mistakes in retrial to maintain authority of ruling and judgment shall be promoted.
20. Strengthening the supervision of level of trial. We will strictly regulate the conditions and number of cases of which the higher court remands for retrial and directs retrial, and improve the mechanism for releasing and interpreting the documents of remanding for retrial and directing retrial and for case information feedback. People's courts that handle the second instance, arraignment, application for retrial, and appeal cases should point out in the judgement document the problems existing in the first instance or the original trial, and clarify the reasons for the judgement.
21. Improving the case quality assessment system. We will establish a scientific and reasonable case quality assessment system. We will abolish the assessment indicators and measures that violate the laws of justice and eliminate any form of ranking. We will strengthen case filing for acceptance by statutory deadlines and case closing within the normal period of trial, establish a long-term pending case notification mechanism, and resolutely stop the wrong practice of artificially controlling the closing of the case. Relying on the disclosure of the trial process, judgement document and enforcement information, we will bring into play the role of the case quality assessment system in serving, judging and guiding the judicial fairness of
22. Deepening the reform of judicial statistics. Guided by the concept of “big data, big pattern and big service”, we will reform the judicial statistics management system, create a system of judicial statistics standard with classified science and comprehensive information, and gradually build an empirical analysis model that meets the actual conditions of trials and the law of justice as well as establish a national court judgments library and a national court justice information big data center.
23. Improving the uniform application mechanism of law. We will improve the methods of trial guidance of the Supreme People's Court and strengthen the standardization, timeliness, pertinence and effectiveness of judicial guidance and other trial guidance methods. We will reform and improve the screening, evaluation and release mechanism of guiding cases. We will improve and perfect the working mechanism for ensuring the uniform application of laws by the people's courts.
24. Deepening the implementation of institutional reforms. We will promote the implementation of the pilot system reform that separates judicial power from enforcement power. We will establish the legal system of credit supervision, deterrence, and punishment for dishonest persons subject to enforcement. We will intensify the reform of judicial auction methods and focus on the implementation of an online judicial auction model. We will improve the enforcement system for execution of property-oriented penalty and promote the implementation of property-oriented penalty in a unified criminal execution system.
25. Promoting the improvement of the judicial aid system. We will clarify the conditions, standards and scope of judicial aid, standardize the acceptance, review and decision of judicial aid, and tighten the management and use of funds. We will promote the national judicial aid legislation, and give full play to the positive role of judicial aid in helping people and resolving conflicts.
26. Deepening international cooperation in the judicial area. We will promote the improvement of the judicial aid system and expand the coverage of interregional and international judicial assistance. We will promote the formulation of the criminal justice assistance law.
(IV) Improving the operating mechanism of judiciary power
To establish a system of operation of
27. Improving the trial procedure for the presiding judge and the collegiate bench. We will select judges with good political qualities, strong case handling skills, high professional standards, and rich judicial experience as presiding judges. The trial in the system of sole-judge proceedings will have the presiding judge as its center. The required number of trial assistants will be provided. In a collegiate system trial, the presiding judge will serve as the chief judge. Where all members of the collegiate bench are presiding judges, in principle, the presiding judge who handles the case serves as the chief judge. We will perfect the working mechanism that the president, division-chief judge and members of the judicial committee serve as the chief judge and participate in case trial by the collegiate bench. We will reform and improve the working mechanism of the collegiate bench, clarify the scope of functions of the collegiate bench as a trial organization, improve the joint participation of members of the collegiate bench in cross file review,
28. Improving the responsibility system of cases handling by the presiding judge and the collegiate bench. In accordance with the principle of integration of power and responsibility, we will clarify the case handling responsibilities and conditions of exemption of the presiding judges, the collegiate bench and its members, and achieve effective connection of evaluation mechanism, accountability mechanism, disciplinary mechanism and exit mechanism as well as protection mechanism. When the presiding judge participates in the collegial discussion as the chief judge, he or she has equal power with other members of the collegiate bench, but he or she will be responsible for presiding over court hearing activities, controlling the trial process, organizing case discussions, and avoiding procedural errors. We will scientifically define the responsibilities of the members of the collegiate bench to ensure that they independently express their opinions and clarify the responsibilities of their personal opinions and performance of their duties in the outcome of the case.
29. Perfecting court president and presiding judge trial management mechanism. We will clarify the trial management responsibilities of the
30. Perfecting court president and presiding judge trial supervision mechanism. We will clarify adjudication supervision duties of the court president and the presiding judge in line with their duties and improve the internal control and supervision mechanism. We will improve the presiding judges meeting and professional judges meeting mechanism. We will standardize the supervision mechanism for major, difficult and complicated cases by the president and the presiding judge, establish a filing system for all the instruments formed by the president and presiding judge during the supervision activities. Relying on modern information technology, we will establish a mechanism that follows the trace, is mutually supervised and controlled throughout the procedure and under which the presiding judge and the collegiate bench exercise the trial power and the president and the division-chief judge exercise the supervision power. We will ensure that supervision is not absent, supervision do not offside, supervision is left with records and any one with misconduct will be held accountable.
31. Perfecting the trial management system. We will give play to the role of protection, promotion and service of trial management in enhancing the quality of trials, standardizing judicial actions, tightening litigation procedures, and unifying proceeding standards. We will strengthen the management of the trial process links and further improve the quality assessment of cases.
32. Reforming the working mechanism of the judicial committee. We will properly position the functions of the judicial committee, and strengthen its macro-guidance functions for summarizing trial experience and discussing and deciding major issues for trial work. We will establish a preemptive filtering mechanism for the matters discussed by the judicial committee and standardize the range of cases discussed by the judicial committee. Except for the circumstances stipulated by law and major complex cases involving state diplomacy, security and social stability, the judicial committee mainly discusses the issue on the application of law in cases. We will perfect the rules of procedure of the judicial committee, and establish the signature verification system for meeting materials and minutes of the judicial committee. We will establish a supervision, reply and publicity system for the resolutions of the judicial committee meetings. We will establish the mechanism for performance assessment of members of the judicial committee and the internal publicity mechanism.
33. Promoting the reform of the people's assessors system. We will implement the "multiplication plan" of the people's assessors, broaden the channels and scope of the selection of people's assessors, ensure the participation of the masses in the judiciary, and ensure that the proportion of grass-roots people is no less than two-thirds of the new people's assessors. We will further standardize the conditions for the selection of people's assessors, reform the method of selection and improve the exit mechanism. We will clarify the power of people's assessors in participation in case trial and improve random drawing mechanism. We will reform the fact that jury system will gradually introduce people’s assessors who will no longer hear the issue of the application of the law and only participate in the issue of fact finding. We will strengthen the funding guarantee for people's assessors performing their duties according to law. We will establish a dynamic management mechanism for people's assessors.
34. Promoting the reasoning reform of judgment documents. According to different levels of trials and types of cases, we will divide complex and simple judgment documents. We will strengthen the reasoning for the judgment documents of first-instance case where the parties involved hold objections, the legal relationship is complex and there is much attention from society, and all the cases of the second-instance, retrial and those determined by discussion of the judicial committee. We will use simple judgment documents for the first-instance civil and commercial cases with clear facts, clear rights and obligations and the least disputes between the parties, and the first-instance minor criminal cases with clear facts, verified and sufficient evidences and guilty pleading by defendants. We will improve the judgment efficiency by filling in the elements and simplifying the format. We will attach importance to the defense and agency opinions of the lawyer. If the lawyer's defense and agency opinion has not been adopted admitted according to law, he or she will explain the reason in the judgment document. We will improve the rigid restraint mechanism and incentive mechanism of reasoning of
35. Improving the judicial supervision mechanism against corruption. We will improve and intensify the work of judicial inspections, trial affair supervision and anti-corruption inspectors. We will establish a mechanism for investigating and punishing violations of disciplines by presiding and lower courts under cooperation with higher discipline inspection commissions and higher courts, and achieve orderly integration of discipline inspection and supervision procedures with judge disciplinary procedures. We will establish a record system and accountability system for interrogating cases by court personnel. We will regulate the contact and communication of court personnel with parties, lawyers, special relationships and intermediary organizations according to law.
36. Reforming the letters and visits system involved in lawsuits. We will perfect the working mechanism of separation of litigation and petition, and clearly define the criteria, scope and procedures for the separation of litigation and petition. We will improve the closing mechanism for letters and visits involved in lawsuits, and standardize the order of letters and visits involved in lawsuits according to law. We will establish the local supervision mechanism for accepting letters and visits and be bold in establishing the online letters and visits handling mechanism. We will promote the establishment of the agency by lawyer system for appeal cases. We will explore the establishment of mechanisms for the participation of the third parties in society and intensify diversified joint efforts to revolve contradictions of letters and visits involved in lawsuits.
(V) Building an open, dynamic, transparent and convenient judicial mechanism
The establishment of a socialist judicial power operation system with Chinese characteristics must rely on modern information technology to build an open, dynamic, transparent and convenient judicial mechanism so as to enhance public understanding, trust and supervision on the judiciary. By the end of 2015, the three major publicity platforms that are judicial process, judgement document and executive information of people’s court with complete system, complete information and convenient for use have been formed, and the comprehensive, systematically scientific judicial mechanism oriented by people has also been established.
37. Improving the open trial system. We will establish the publicity and appointment system for trial notice and auditor seat information. The people’s court will give priority to the court which should be adapted to the number of auditors who have been applied to the court with respect to the cases should be heard in public in accordance with the law and are concerned by the society. The conditional courts will set up a media auditorium to give priority to satisfying the needs of the news media.
38. Improving the trial process publicity platform. We will promote the construction of the National Court Affairs website and establish the litigation notice online handling platform and litigation notice website unified by national courts. The construction of China’s trial process information disclosure website will be continue strengthened to improve the mechanism of timely collection and immediate updating of trial information data. The construction of electronization of litigation files will be speeded up. The national courts will be encouraged to
39. Improving the judgement document publicity platform. We will strengthen the website construction of China Judgments Online to improve its function of querying, searching and aggregating information, so as to facilitate the public to effectively acquiring, accessing and copying the judgement documents. In strict accordance with the requirements of “publicity as the principle and non-publicity as the exception”, the judgement document in force that should be published by people's court at four levels in accordance with the law will be published in the China Judgments Online.
40. Improving the executive information disclosure platform. The national courts will be encouraged to publish executive information on the same platform by integrating all kinds of executive information, so as to facilitate the parties to understand the progress of implementation online. Furthermore, we will strengthen the information disclosure about dishonest person subject to enforcement to give full play to their credit disciplinary function and urge the person subject to enforcement to perform the effective legal instruments automatically. We will also enhance the construction of information disclosure system for the person subject to enforcement to facilitate the public to understand the implementation and take the initiative to accept social supervision.
41. Improving the commutation, parole, temporary execution outside prison publicity system. We will improve the conditions suitable for commutation, parole, temporary execution outside prison and the procedures for handling cases, so as to ensure that the relevant cases are handled in open and fair principle. In conjunction with the penal executive and procuratorial organs to promote the construction of an online collaborative handling case platform, the important items and key links in the execution of law enforcement and evaluation of rewards and punishments will be published, shared and recorded on the website, so as to ensure supervision in place from the system and technology. In addition, establishing the information network of commutation, parole, temporary execution outside prison will be our major task to achieve the case filing notice, trail announcement and instruments of the three categories of cases are published online.
42. Establishing judicial public supervision system. We will encourage the public to supervise the judicial publicity and the complaint mechanism and relief channels for violating judicial public provisions will be sound. With fully use of the supervision function of the three major judicial openness platforms, the opinions and suggestions proposed by the public on platform will become the important reference for the trial management, trial supervision and work improvement of people's court.
43. Improving the litigation service center system. We will strengthen the standardization construction of litigation service center to improve the litigant service hall, online litigation service platform and judicial service hotline (12368). We will also establish the online booking for case filing, service, announcement, complaints and other working mechanisms. The remote mediation, petition and other video applications will be vigorously used to further expand the breadth and depth of justice for the people.
44. Improving the people’s court system. We will optimize the regional layout and personnel ratio of the people's court and actively promote the layout form of court oriented by central court and supplemented by community court and circuit trial place. We will also improve the case filing mechanism of people's court s for the convenience of the people according to the actual situation of the jurisdiction and optimize the personnel composition of the people's court. In addition, we will conduct the personnel exchanges between the people's courts, people's courts and other halls of basic people's courts orderly.
45. Promoting the service system reform. We will push the restriction mechanism in which the parties should confirm the address for service and undertake the corresponding legal consequences, and explore the electronic delivery mode under the condition of information promotion so as to improve the efficiency of service.
46. Improving the diversified dispute resolution mechanism. We will further promote the organic connection and coordination of the dispute settlement mechanism and litigation, such as mediation, arbitration, administrative adjudication and administrative reconsideration, thus guiding the parties to choose appropriate dispute settlement methods. In the field of land expropriation, environmental protection, labor security, medical and health, traffic accidents, property management, insurance disputes and so on, we will enhance the construction of industrial and professional dispute resolution organizations to promote the perfection of the arbitration and administrative adjudication system. We will establish a joint working system for people's mediation, administrative mediation, industrial mediation, commercial mediation and judicial mediation, and drive the legislative process of diversified dispute resolution mechanism to establish a systematically and scientifically diversified dispute resolution system.
47. Promoting the implementation of law popularity responsibility system. We will strengthen the consciousness of the law popularity by court, and fully utilize the law popularity function produced from the open trial, reasoning by documents and publication of cases to promote the high unity of the people's court to exercise the judicial function and fulfill the responsibility of law popularity.
(VI) Promoting the normalization, specialization and professionalization of court officials
The establishment of a socialist judicial power operation system with Chinese characteristics must be centered with trial and focused on the judge to promote the standardization, specialization and professionalization of court officials in an all-round way, and strive to improve the professional quality and level. By the end of 2017, the court official management system with a scientific classification, clear division of labor, reasonable structure and conforming to the professional characteristics of justice had been initially established.
48. Promoting the reform of classification management system of court officials. We will establish a separate job sequence for judges with professional characteristics and improve the management system of trial assistant, such as judge assistant, clerk and executor. The proportion of judges and trial assistants will be scientifically determined, and a normal supplementary mechanism for trial assistants will be established in order to effectively reduce the workload of judges. The sources of trial assistants will be broadened to optimize the structure of trial assistants by exploring ways to purchase social services. Additionally, we will explore and promote the judicial police management system, as well as improve the administration system of judicial administrative personnel.
49. Establishing the specified number of judge system. According to the economic and social development, population size (including temporary population), number of cases, type of cases and other basic data in the jurisdiction of the court, we will scientifically determine the specified number of judge in courts at four levels in combination with the functions of the court, workload of the judges, allocation of trial assistant, guarantee conditions for handling case and other factors. The dynamic adjustment mechanism of specified number of judge will be improved as per the number of cases and changes in personnel structure. To ensure that excellent judges remain on the frontline of the trial, we will set up the interim scheme for reform of specified number of judge system in a comprehensive and scientific way, taking into account the factors such as trial performance, business capability, theoretical level and work experience.
50. Reforming the judge elective system. We will set up qualifications of different judges for different levels of court. At the national and provincial level, a Judge Selection Committee, with the participation of judge representatives and social related personnel, will be set up separately to establish an open, fair and just elective procedure to ensure that outstanding legal personnel with good conduct, rich experience and higher professional level become candidates, such that the judge selection mechanism and the statutory appointment and removal mechanism can be effectively linked. We will complete the mechanism in which the newly appointed judges are recruited by the Higher People's Court and serve the Basic People's Court. We will improve the training system for reserved judges in line with the reform of the unified pre-service training system for legal professionals. The age of the newly appointed judge will be appropriately raised. We will establish the working mechanism in which the judge from superior court is selected from the lower court in principle, and perfect the system of appointing outstanding lawyers, legal scholars, and professional legal personnel serving in the legislative, procuratorial and law enforcement departments as judges. Finally, the two-way communication mechanism between court, law schools and legal research institutions personnel will be improved to implement the mutually engagement plan of universities and court officials.
51. Improving the judge performance evaluation system. We will establish a scientific and rational, objective and fair judge performance evaluation system consistent with rules to improve the evaluation criteria, and take the evaluation results as an important basis for the grade promotion and preferential selection of judges. We will also establish the exit mechanism of incompetent judges to improve relevant supporting measures.
52. Improving the on-the-job training mechanism of judges. We will focus on enhancing the judge's ability to handle the trial, apply the law and writing ability of judgement document strictly being oriented by the actual demands, adhering to the classification, grading and all staff training. We will improve the plan preparation, organizational training, tracking management and quality evaluation mechanism of education and training on judge. Furthermore, we will perfect the teaching staff, case base and excellent courseware library and strengthen the construction of judge training institution and on-site teaching bases. The China judge education and training network will also be established to achieve high-quality courseware free online shared by court officials relying on information technology and vigorously promoting online teaching. Efforts will be made to strengthen the training of judges at the grass-roots level and bilingual judges of ethnic minorities.
53. Improving the judge wage system. To implement the provisions in the Judge-made Law, we will research and establish the wage system matching the separate duties of judge.
(VII) Ensuring
To establish a socialist judicial power operation system with Chinese characteristics, the various systems will be promoted and improved to ensure that the people's court will exercise judicial power independently and impartially in accordance with the law under the leadership of the Party, to optimize the judicial environment, establish judicial authority, strengthen the occupational security and improve the credibility of the judiciary. By the end of 2018, the system environment and social atmosphere of reliance on justice, respect for justice and support for justice will be promoted.
54. Promoting unified management reform of court officials below provincial level. In line with the relevant departments of the
55. Establishing a working mechanism to prevent the intervention of judicial activities. We will, in accordance with the relevant departments of the Central Government, promote the system for leading cadres to intervene in trial activities and step in records, notifications and accountability for handling specific cases. According to the requirements of recording cases in whole course, the record obligation and responsibility of the judicial organization will be clearly defined, and the leading cadres will be involved in the judicial activities, instructions, letters, records and other information of the specific cases. The mechanism of legal access, storage of media, entry of the special library, and filing for reference will be established, and the relevant information will be stored in the original document about case for access of parties and their agents.
56. Improving the protection mechanism for the judges to perform their legal duties. We will reasonably determine the duties, working procedures and working standards of judges and trial assistants. We will clarify the selection criteria and exemption reasons for different subjects and different types of fault, so as to ensure that judges perform their duties according to law without investigation. Without statutory circumstances, judges shall not be transferred or dismissed, or removed or demoted. We will improve the system of judges' appealing and accusation, establish a relief mechanism for judges' legitimate rights and interests being infringed upon by their duties according to law, and improve the mechanism of false reporting and clarification. At the national and provincial level, the judge disciplinary committee, which is composed of judges' representatives and social related personnel, is set up respectively to make open and impartial procedures for the punishment of judges, not only to ensure that the judge who violates rule and law will be punished in time, but also to guarantee the rights of justification, proof, reconsideration and appeal.
57. Perfecting the judicial authority guarantee mechanism. We will improve the prosecution mechanism for refusing to execute judgments, rulings, contempt of court authority and other criminal acts. We will also promote relevant legal amendments and punish the personnel who destroy evidence materials, court records, legal documents, court facilities in court and have other behavior with seriously contempt of court, as well as have the criminal acts, such as threatening, insulting, tracking, harassing the court officials or their immediate family, etc. in accordance with law.
58. Strengthening the guarantee mechanism of litigation integrity. We will establish the record and punishment system of litigation integrity. In accordance with the law, we will punish the false litigation, malicious litigation and unreasonable repeated-appealing which will be incorporated into the social credit system. We will explore the establishment of suit for damage for victim from false litigation and malicious litigation.
59. Optimizing the external environment of administrative trial. We will improve the system of responding to lawsuits by head of administrative organs, guide and regulate administrative organs to participate in litigation activities. We will also standardize the preparation and submission of judicial proposals to promote the level of law-based administration of government.
60. Perfecting the judge oath system. We will improve the judge oath system. The judges elected or appointed by the NPC at different levels and their standing committees shall make a vow publicly to the constitution.
61. Improving the judicial honor system. We will clearly define the criteria, conditions and procedures for conferring judges and adjudication assistant on different categories so as to enhance the sense of honor and belonging of the judicial profession for court officials.
62. Straightening out the relationship of judicial administrative affairs management of the court. We will scientifically set up judicial administrative affairs administration organ of the People's Court to standardize and unify the responsibilities of management, and to explore the relative separation of the administrative power of the judicial administrative affairs and the judicial power of the court. We will improve the judicial administrative affairs administration mechanism of the higher and lower courts, and make clear the supervisory functions of the judicial administrative affairs administration department of higher courts to the judicial administrative affairs of the lower courts.
63. Promoting the reform of the property management system of people's court. In line with the relevant departments of the
64. Promoting the reform of internal organization in the people's court. In accordance with the scientific, streamlined and efficient work requirements, we will promote flat management and gradually set up the setting model of internal organization in court focusing on service trial.
65. Promoting the information construction of the people's court. We will speed up the construction of “balance project”, focus on integrating existing resources, and promote all kinds of information applications that serve the court and public demands. The coverage rate of the main business information of the Supreme People's Court and the Higher People's Court shall reach 100%, and the Intermediate People's Court and the Basic People's Court shall be more than 95% and 85%, respectively.
IV. Comprehensively Deepening the Work Requirements of People's Court Reform
Comprehensively deepening the reform of the people's court is an arduous task, with great responsibilities and time constraints. The people's courts at all levels shall conscientiously carry out the decision and deployment of theCentral Government, strengthen the organization and leadership, improve the working mechanism, carry out and promote the work in a key, step and orderly way to ensure the actual effect of the reform measures and the achievements of the reform to benefit all the people.
The judicial reform leading group of the Supreme People’s Court is a deliberative, coordinating and guiding institution for the judicial reform of the people’s court. The regular group meeting shall be held to study and determine the key points of the reform, consider the reform scheme, listen to the progress report and discuss the major issues.
The Supreme People's Court will establish the system of information sharing, supervision and examination, and evaluation and summary, to promptly grasp the reform dynamics, strengthen the supervision and guidance, correct the wrong practice, and summarize the successful experience, so that every reform task will be arranged, supervised and inspected, so as to ensure that all the tasks are not broken down.
The Higher People’s Court shall set up a judicial reform leading group to supervise, guide and coordinate the judicial reform of the courts within the jurisdiction. The people's courts at all levels shall establish and improve the system of filing and reporting of judicial reform, and sum up the experience of the reform, report the work progress and reflect the difficulties and problems in time. Where the Higher People’s Court will carry out a pilot project on some of the reform projects, the pilot scheme must be submitted to the Supreme People’s Court for approval, and the pilot scheme for major reform must be submitted to the central government by Supreme People’s Court for approval prior to implementation.
Supreme People’s Court
February 4, 2015
最高人民法院关于进一步推进案件繁简分流优化司法资源配置的若干意见
法发〔2016〕21号
为进一步优化司法资源,提高司法效率,促进司法公正,减少当事人诉讼成本,维护人民群众合法权益,根据《中华人民共和国民事诉讼法》《中华人民共和国刑事诉讼法》《中华人民共和国行政诉讼法》等法律规定,结合人民法院工作实际,现就进一步推进案件繁简分流、优化司法资源配置提出如下意见。
1.遵循司法规律推进繁简分流。科学调配和高效运用审判资源,依法快速审理简单案件,严格规范审理复杂案件,实现简案快审、繁案精审。根据案件事实、法律适用、社会影响等因素,选择适用适当的审理程序,规范完善不同程序之间的转换衔接,做到该繁则繁,当简则简,繁简得当,努力以较小的司法成本取得较好的法律效果。
2.推进立案环节案件的甄别分流。地方各级人民法院根据法律规定,科学制定简单案件与复杂案件的区分标准和分流规则,采取随机分案为主、指定分案为辅的方式,确保简单案件由人民法庭、速裁团队及时审理,系列性、群体性或关联性案件原则上由同一审判组织审理。对于繁简程度难以及时准确判断的案件,立案、审判及审判管理部门应当及时会商沟通,实现分案工作的有序高效。
3.完善送达程序与送达方式。当事人在纠纷发生之前约定送达地址的,人民法院可以将该地址作为送达诉讼文书的确认地址。当事人起诉或者答辩时应当依照规定填写送达地址确认书。积极运用电子方式送达;当事人同意电子送达的,应当提供并确认传真号、电子信箱、微信号等电子送达地址。充分利用中国审判流程信息公开网,建立全国法院统一的电子送达平台。完善国家邮政机构以法院专递方式进行送达。
4.发挥民事案件快速审判程序的优势。根据民事诉讼法及其司法解释规定,积极引导当事人双方约定适用简易程序审理民事案件。对于标的额超过规定标准的简单民事案件,或者不属于民事诉讼法第一百五十七条第一款规定情形但标的额在规定标准以下的民事案件,当事人双方约定适用小额诉讼程序的,可以适用小额诉讼程序审理。依法适用实现担保物权案件特别程序。积极引导当事人将债权人请求债务人给付金钱、有价证券的案件转入督促程序,推广使用电子支付令。
5.创新刑事速裁工作机制。总结刑事速裁程序试点经验,加强侦查、起诉、审判程序的衔接配合。推广在看守所、执法办案单位等场所内建立速裁办公区,推动案件信息共享及案卷无纸化流转,促进案件办理的简化提速。
6.简化行政案件审理程序。对于已经立案但不符合起诉条件的行政案件,经过阅卷、调查和询问当事人,认为不需要开庭审理的,可以径行裁定驳回起诉。对于事实清楚、权利义务关系明确、争议不大的案件,探索建立行政速裁工作机制。
7.探索实行示范诉讼方式。对于系列性或者群体性民事案件和行政案件,选取个别或少数案件先行示范诉讼,参照其裁判结果来处理其他同类案件,通过个案示范处理带动批量案件的高效解决。
8.推行集中时间审理案件的做法。对于适用简易程序审理的民事案件、适用速裁程序或者简易程序审理的轻微刑事案件,实行集中立案、移送、排期、开庭、宣判,由同一审判组织在同一时段内对多个案件连续审理。
9.发挥庭前会议功能。法官或者受法官指导的法官助理主持召开庭前会议,解决核对当事人身份、组织交换证据目录、启动非法证据排除等相关程序性事项。对于适宜调解的案件,积极通过庭前会议促成当事人和解或者达成调解协议。对于庭前会议已确认的无争议事实和证据,在庭审中作出说明后,可以简化庭审举证和质证;对于有争议的事实和证据,征求当事人意见后归纳争议焦点。
10.创新开庭方式。对于适用简易程序审理的民事、刑事案件,经当事人同意,可以采用远程视频方式开庭。证人、鉴定人、被害人可以使用视听传输技术或者同步视频作证室等作证。
11.推行庭审记录方式改革。积极开发利用智能语音识别技术,实现庭审语音同步转化为文字并生成法庭笔录。落实庭审活动全程录音录像的要求,探索使用庭审录音录像简化或者替代书记员法庭记录。
12.推进民事庭审方式改革。对于适用小额诉讼程序审理的民事案件,可以直接围绕诉讼请求进行庭审,不受法庭调查、法庭辩论等庭审程序限制。对于案件要素与审理要点相对集中的民事案件,可以根据相关要素并结合诉讼请求确定庭审顺序,围绕有争议的要素同步进行法庭调查和法庭辩论。
13.探索认罪认罚案件庭审方式改革。对于被告人认罪认罚的案件,探索简化庭审程序,但是应当听取被告人的最后陈述。适用刑事速裁程序审理的,可不再进行法庭调查、法庭辩论;适用刑事简易程序审理的,不受法庭调查、法庭辩论等庭审程序限制。
14.促进当庭宣判。对于适用小额诉讼程序审理的民事案件、适用速裁程序审理的刑事案件,原则上应当当庭宣判。对于适用民事、刑事、行政简易程序审理的案件,一般应当当庭宣判。对于适用普通程序审理的民事、刑事、行政案件,逐步提高当庭宣判率。
15.推行裁判文书繁简分流。根据法院审级、案件类型、庭审情况等对裁判文书的体例结构及说理进行繁简分流。复杂案件的裁判文书应当围绕争议焦点进行有针对性地说理。新类型、具有指导意义的简单案件,加强说理;其他简单案件可以使用令状式、要素式、表格式等简式裁判文书,简化说理。当庭宣判的案件,裁判文书可以适当简化。当庭即时履行的民事案件,经征得各方当事人同意,可以在法庭笔录中记录相关情况后不再出具裁判文书。
16.完善二审案件衔接机制。积极引导当事人、律师等提交电子诉讼材料,推进智慧法院建设和诉讼档案电子化,运用电子卷宗移送方式,加快案卷在上下级法院之间的移送。优化二审审理方式,围绕诉讼各方争议问题进行审理,避免二审与一审在庭审和裁判文书方面的不必要重复。强化二审统一裁判尺度、明确裁判规则等功能。
17.提升人案配比科学性。在精确测算人员、案件数量和工作量的基础上,动态调整不同法院、不同审判部门的审判力量。根据法院审级、案件繁简等相关因素,合理确定法官、法官助理、书记员的配置比例,科学界定各自职能定位及其相互关系,最大程度地发挥审判团队优势。
18.推广专业化审判。在充分考虑法官办案能力、经验及特长等因素的基础上,根据案件的不同类型确定审理类型化案件的专业审判组织,根据案件的繁简程度确定专门审理简单案件与复杂案件的审判人员。推进办案标准化建设,健全案例工作制度。构建法官轮岗机制,完善业绩评价体系,激发和保持审判队伍的活力。
19.推进审判辅助事务集中管理。根据审判实际需要,在诉讼服务中心或者审判业务等部门安排专门的审判辅助人员,集中负责送达、排期开庭、保全、鉴定评估、文书上网等审判辅助事务。
20.完善多元化纠纷解决机制。推动综治组织、行政机关、人民调解组织、商事调解组织、行业调解组织、仲裁机构、公证机构等各类治理主体发挥预防与化解矛盾纠纷的作用,完善诉调对接工作平台建设,加强诉讼与非诉纠纷解决方式的有机衔接,促进纠纷的诉前分流。完善刑事诉讼中的和解、调解。促进行政调解、行政和解,积极支持行政机关依法裁决同行政管理活动密切相关的民事纠纷。
21.发挥律师在诉讼中的作用。积极支持律师依法执业,保障律师执业权利,重视律师对案件繁简分流和诉讼程序选择的意见,积极推动律师参与调解、代理申诉等工作。
22.引导当事人诚信理性诉讼。加大对虚假诉讼、恶意诉讼等非诚信诉讼行为的打击力度,充分发挥诉讼费用、律师费用调节当事人诉讼行为的杠杆作用,促使当事人选择适当方式解决纠纷。当事人存在滥用诉讼权利、拖延承担诉讼义务等明显不当行为,造成诉讼对方或第三人直接损失的,人民法院可以根据具体情况对无过错方依法提出的赔偿合理的律师费用等正当要求予以支持。
最高人民法院
2016年9月12日
Opinions of the Supreme People’s Court on Further Promoting Division of Complexity and Simplicity for Cases and Optimizing Judicial Resource Allocation
No. 21 [2016] of the Supreme People’s Court
To further optimizejudicial resource, improvejudicial efficiency, promotejudicial fairness, reducelitigation cost of the parties and maintain legitimate rights and interests of the masses, the following opinions on further promoting the division of complexity andsimplicity forcases and optimizing the judicial resource allocation are proposed pursuant to the
1. Promoting the division of complexity andsimplicity according to the judicial disciplines. We will hear the simple cases quickly according to the law through the scientific allocation and efficient application of
2. Promoting the screening and division of cases when filing.Local people's court atdifferent levels shall formulate distinguish standard and division rules of simple and complex cases scientifically according to the
3. Improving service procedure and methods. If the parties appoint the service address before the dispute occurs, the people's court may use this address as the confirmation address for serving the litigation documents. When a party sues or replies,the confirmation letter of the service address shall be filled in according to the regulations. Service shall be realizedelectronically.If the parties agree the electronicservice, they shall provide and confirm the electronic service addresses such as fax numbers, E-mail, Wechat ID, etc. We shall make full use of China Judicial Process Information Online and establish a unified electronic service platform for national courts. Improving national postal service shall be delivered by special mailing for court.
4. Giving full play to the advantages of thequick trial procedure in civil cases. According to the provisions of the Civil Procedure Law and its
5. Innovating the fast-tracksentencing mechanism forcriminalcases. We should summarizethe pilot experience of criminal fast-tracksentencing procedure, strengthen connection and cooperation of investigation, prosecution and trial procedure, generalize the establishment offast-track sentencing office at
6. Simplifying trial procedure ofadministrative case.For administrative cases which have been filed but are not in line with the conditions of prosecution, if it is considered that no trial is required after
7. Exploring the way to implement test case.For serial or group civil and administrative cases, we shall select individual or few cases to implement test case first, and handle
8. Carrying out
9. Giving full play to the meeting function before trail. The judge or the judge's assistant under the guidance of the judgeshall preside over the meeting before trial to solve the relevant procedural matters such as checking the identity of the parties, organizing the exchange of evidence catalogues, and starting the exclusionary rule of illegal evidence. For cases that are suitable for mediation, the reconciliation of the parties or the
10. Innovating the way to open a court session. For the civil and criminal cases that are heard for
11. Carrying out the reform of the way of court hearing record. We shall actively develop and useintelligent speech recognition technology to translate voice in the court hearing into words and generate court records, implementthe requirements for fullvoice and video& audiorecording in court hearing, explore and use court hearing audio and video recording to simplify or replace court records of
12. Promoting the reform ofthe way of civil court hearing. For civil cases that areheard for small claims proceedings, it is possible to conduct a court hearing directly around the litigation request, without being restricted by court hearing procedures such as court investigation, court debate, etc. With regard to civil cases with relatively concentrated elements of cases and points of trial, the court order can be determined according to the relevant elements and the litigation request, and the court investigation and court debate shall be carried out synchronously around the controversial elements.
13. Exploring the reform of court hearing methods of confession and
14. Promoting the sentence in the court. For thecivil cases that are heard for thesmall claims procedure and the
15. Implementing the division of complexity and simplicity for judgement document. According to theinstance of court, case type and court hearing, the division of complexity andsimplicity shall be carried out for the system and the structure as well as reasoning of the judgement document. The judgement document of complex cases shall be arguedspecifically around the
16. Improving
17. Promoting the
18. Popularizing professional trial.On the basis of full consideration of judges' handling ability, experience and expertise,the professional trial organizations forhearing categorization cases shall be determined according to different types ofthe cases, and the adjudicatory personnel in charge of hearing simple and complex cases shall be determined according to the complexity andsimplicity extent of the case. We shall promote the standardization construction of handling cases,improve the system of case work, establishjudge rotation mechanism,and improve performance evaluation system to stimulate and maintain the vitality of the trial team.
19. Promoting the
20. Improving diversified dispute settlement mechanism. We shall promote all kinds of governance bodies, such as comprehensive governance organization, administrative organs, people's mediation organizations, commercial mediation organizations, industrial mediation organizations, arbitration institutions and the notary institutions, toplay the role of preventing and resolving contradictions and disputes, improve the construction of platform of dockinglitigation andconciliation, and strengthenorganic connection between litigation and non-litigation dispute settlement to promote the division
21. Giving full play to the role of lawyers in litigation. We shall actively support
22. Guiding the parties to
Supreme People's Court
September 12, 2016
最高人民法院关于人民法院通过互联网公开审判流程信息的规定 法释[2018]7号
《最高人民法院关于人民法院通过互联网公开审判流程信息的规定》已于2018年2月12日由最高人民法院审判委员会第1733次会议通过,现予公布,自2018年9月1日起施行。
最高人民法院
二○一八年三月四日
最高人民法院关于人民法院通过互联网公开审判流程信息的规定
(2018年2月12日最高人民法院审判委员会第1733次会议通过,自2018年9月1日起施行)
为贯彻落实审判公开原则,保障当事人对审判活动的知情权,规范人民法院通过互联网公开审判流程信息工作,促进司法公正,提升司法公信,根据《中华人民共和国刑事诉讼法》《中华人民共和国民事诉讼法》《中华人民共和国行政诉讼法》《中华人民共和国国家赔偿法》等法律规定,结合人民法院工作实际,制定本规定。
第一条 人民法院审判刑事、民事、行政、国家赔偿案件的流程信息,应当通过互联网向参加诉讼的当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开。
人民法院审判具有重大社会影响案件的流程信息,可以通过互联网或者其他方式向公众公开。
第二条 人民法院通过互联网公开审判流程信息,应当依法、规范、及时、便民。
第三条 中国审判流程信息公开网是人民法院公开审判流程信息的统一平台。各级人民法院在本院门户网站以及司法公开平台设置中国审判流程信息公开网的链接。
有条件的人民法院可以通过手机、诉讼服务平台、电话语音系统、电子邮箱等辅助媒介,向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人主动推送案件的审判流程信息,或者提供查询服务。
第四条 人民法院应当在受理案件通知书、应诉通知书、参加诉讼通知书、出庭通知书中,告知当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人通过互联网获取审判流程信息的方法和注意事项。
第五条 当事人、法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人的身份证件号码、律师执业证号、组织机构代码、统一社会信用代码,是其获取审判流程信息的身份验证依据。
当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人应当配合受理案件的人民法院采集、核对身份信息,并预留有效的手机号码。
第六条 人民法院通知当事人应诉、参加诉讼,准许当事人参加诉讼,或者采用公告方式送达当事人的,自完成其身份信息采集、核对后,依照本规定公开审判流程信息。
当事人中途退出诉讼的,经人民法院依法确认后,不再向该当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开审判流程信息。
法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人参加诉讼或者发生变更的,参照前两款规定处理。
第七条 下列程序性信息应当通过互联网向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开:
(一)收案、立案信息,结案信息;
(二)检察机关、刑罚执行机关信息,当事人信息;
(三)审判组织信息;
(四)审判程序、审理期限、送达、上诉、抗诉、移送等信息;
(五)庭审、质证、证据交换、庭前会议、询问、宣判等诉讼活动的时间和地点;
(六)裁判文书在中国裁判文书网的公布情况;
(七)法律、司法解释规定应当公开,或者人民法院认为可以公开的其他程序性信息。
第八条 回避、管辖争议、保全、先予执行、评估、鉴定等流程信息,应当通过互联网向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开。
公开保全、先予执行等流程信息可能影响事项处理的,可以在事项处理完毕后公开。
第九条 下列诉讼文书应当于送达后通过互联网向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开:
(一)起诉状、上诉状、再审申请书、申诉书、国家赔偿申请书、答辩状等诉讼文书;
(二)受理案件通知书、应诉通知书、参加诉讼通知书、出庭通知书、合议庭组成人员通知书、传票等诉讼文书;
(三)判决书、裁定书、决定书、调解书,以及其他有中止、终结诉讼程序作用,或者对当事人实体权利有影响、对当事人程序权利有重大影响的裁判文书;
(四)法律、司法解释规定应当公开,或者人民法院认为可以公开的其他诉讼文书。
第十条 庭审、质证、证据交换、庭前会议、调查取证、勘验、询问、宣判等诉讼活动的笔录,应当通过互联网向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开。
第十一条 当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人申请查阅庭审录音录像、电子卷宗的,人民法院可以通过中国审判流程信息公开网或者其他诉讼服务平台提供查阅,并设置必要的安全保护措施。
第十二条 涉及国家秘密,以及法律、司法解释规定应当保密或者限制获取的审判流程信息,不得通过互联网向当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人公开。
第十三条 已经公开的审判流程信息与实际情况不一致的,以实际情况为准,受理案件的人民法院应当及时更正。
已经公开的审判流程信息存在本规定第十二条列明情形的,受理案件的人民法院应当及时撤回。
第十四条 经受送达人书面同意,人民法院可以通过中国审判流程信息公开网向民事、行政案件的当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人电子送达除判决书、裁定书、调解书以外的诉讼文书。
采用前款方式送达的,人民法院应当按照本规定第五条采集、核对受送达人的身份信息,并为其开设个人专用的即时收悉系统。诉讼文书到达该系统的日期为送达日期,由系统自动记录并生成送达回证归入电子卷宗。
已经送达的诉讼文书需要更正的,应当重新送达。
第十五条 最高人民法院监督指导全国法院审判流程信息公开工作。高级、中级人民法院监督指导辖区法院审判流程信息公开工作。
各级人民法院审判管理办公室或者承担审判管理职能的其他机构负责本院审判流程信息公开工作,履行以下职责:
(一)组织、监督审判流程信息公开工作;
(二)处理当事人及其法定代理人、诉讼代理人、辩护人对审判流程信息公开工作的投诉和意见建议;
(三)指导技术部门做好技术支持和服务保障;
(四)其他管理工作。
第十六条 公开审判流程信息的业务规范和技术标准,由最高人民法院另行制定。
第十七条 本规定自2018年9月1日起施行。最高人民法院以前发布的司法解释和规范性文件与本规定不一致的,以本规定为准。
Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Disclosure of Trial Procedure Information by the People’s Courts on Line Interpretation No. 7 [2018] of the Supreme People's Court
The Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Disclosure of Trial Procedure Information by the People’s
The Supreme People’s Court
March 4, 2018
Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Disclosure of Trial Procedure Information by the People’sCourts on Line
(Adopted at the 1733th Session of the Judicial Committee of the Supreme People’s Court on February 12, 2018, and effective as of September 1, 2018)
To implement open trial principle, safeguard the right of the parties involved to know the activities associated with the trial, standardize the publicizing of trial information by the people’s courts on line, promote judicial fairness and enhance judicial credibility, the Regulations are hereby formulated in accordance with Criminal Procedure Law of the People’s Republic China, Civil Procedure Law of the People’s Republic of China, Administrative Procedure Law of the People’s Republic of China, State Compensation Law of the People’s Republic of China, etc., by combination with the actual work situation of the people’s courts.
Article 1 The people’s courts shall disclose the trial procedure information about criminal, civil, administrative and state compensation cases to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line.
The people’s courts may disclose trial procedure information of cases with significant social influence to the public on line or by other means.
Article 2 The people’s courts shall disclose procedure information associated with trial on line in a legal, standardized and timely manner to make convenient for the public.
Article 3 China Judicial Process Information Online is the unified platform for the people’s courts to disclose trial procedure information. The people’s courts at all levels shall provide link to China Judicial Process Information Online on its own website and open judicial platform.
The people’s courts may proactively push trial procedure information about cases or provide inquiry services to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders by telephone, lawsuit service platform, telephone-voice system, email and other supporting media if possible.
Article 4 The people’s courts shall inform the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders of method and notes about obtaining trial procedure information in case acceptance notice,notice of responding to action, notice of participating lawsuit and notice of appearance.
Article 5 ID card number, lawyer practicing certificate number, organization code and unified social credit code are the authentication basis for the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders to obtain trial procedure information.
The parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders shall cooperate with the people’s courts accepting the cases to collect and check identity information and shall reserve the effective telephone number.
Article 6 Where the people’s courts inform the parties involved of responding to action and participating the action and allow the parties involved to participate the actions or deliver the notices to the parties involved through announcement, then after collecting and checking the identy information of the parties involved, the people’s courts shall disclose trial procedure informaiton as stipulated herein.
The people’s courts will no longer disclose the trial procedure information to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders in case that the parties involved quit the lawsuit which has been confirmed by the people’s courts.
In case that the statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders participate the lawsuit or change, then the preceding two articles shall be referred to for disposal.
Article 7 The people’s courts shall disclose the following procedural information to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line.
(I) Information about cases acceptance, filing and settlement;
(II) Information about procuratorial organ, criminal punishments execution organ and the parties involved;
(III)Information about judicial organization;
(IV) Information about trial procedures, trial period, service, appeal, protesting, transfer, etc.
(V) Date and place of litigious activities such as court trial, cross-examination, evidence exchange, pretrial conference, inquiry, sentence, etc.
(VI) Information about disclosure of judgment document in China Judgments Online;
(VII) Other procedural information that shall be disclosed as stipulated by laws and judicial interpretation or that the people’s courts consider necessary to disclose.
Article 8 The people’s courts shall disclose the procedure information about withdrawal,dispute governing, preservation, advanced execution, assessment and authentication, etc. to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line.
Where disclosure of procedure information about preservation, advanced execution, etc. might influence case disposal, then those procedure information may be disclosed after the case disposal.
Article 9 The people’s courts shall disclose the following litigation document to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line after service.
(I) Litigation documents, such as indictment form, petition for appeal, petition, appeal form, national compensation application form, and pleadings;
(II) Litigation documents, such as case acceptance notice, notice of responding to action, notice of participating lawsuit, notice of appearance, notice of members of collegiate panel, summons, etc.
(III) Written judgment, written verdict, written decision, mediation document as well as judgment documents about suspension or termination of lawsuit, or that significantly influence the substantive right and procedural rights of the parties involved;
(IV) Other litigation documents that shall be disclosed as stipulated by laws and judicial interpretation or that the people’s courts consider necessary to disclose.
Article 10 The people’s courts shall disclose the contents of records about litigious activities, such as court trial,cross-examination,evidence exchange,pretrial conference,inquiry, sentence to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line.
Article 11 Where the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders apply for consulting video and audio recording and electronic portfolio about court trial, the people’s courts may make it available on China Judicial Process Information Online or on other lawsuit service platforms and set neccessary safety protection measures.
Article 12 The people’s courts shall not disclose trial procedure information that involve state secrets and that shall be kept confidential or restricted as stipulated by laws and judicial interpretation to the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders on line.
Article 13 In case of any inconsistency between the disclosed trial procedure information and the actual situation, the actual situation shall prevail; and the people’s courts accepting the case shall make correction in a timely manner.
Where the disclosed trial procedure information meets the conditions mentioned in Article 12, the people’s courts accepting the case shall withdraw the information in a timely manner.
Article 14 Upon written consent by the addressee, the people’s courts may electronically deliver litigation documents rather than written judgment, written verdict, mediation document through China Judicial Process Information Online to the parties involved, statutory agent, agent ad litem.
In case of service by means mentioned in the preceding article, the people’s courts shall collect and check identity information of the addressee and open exclusive instant messaging system for the addressee in accordance with Article 5 of the Regulations. The date that the litigation documents reach the system shall be deemed as the date of service; and the system will automatically record and generate proof of service which shall be filed in electronic portfolio.
Litigation documents that have been serviced but require correction shall be re-serviced.
Article 15 The Supreme People’s Court shall supervise and provide guidance on the disclosure of trial procedure information of all courts in China. Superior people’s courts and intermediate people’s courts shall supervise and provide guidance on the disclosure of trial procedure information of all district courts.
Trial management offices or other organs undertaking the trial management in the people’s courts at all levels shall be responsible for the disclosure of the trial procedure information of the court and implement the following duties:
(I) Organize and supervise the disclosure of trial procedure information;
(II) Dispose the complaints and suggestions put forward by the parties involved in lawsuit, their statutory agents, agents ad litem and defenders about trial procedure information;
(III) Guide technical department to conduct technical support and service assurance;
(IV) Other management tasks
Article 16 Service specifications and technical standards about disclosure of trial procedure information will be separately formulated by the Supreme People’s Court.
Article 17 The Regulations shall be implemented from September 1, 2018. In the event of any discrepancy between judicial interpretations and normative documents previously promulgated by the Supreme People’s Court and these Regulations, the Regulations shall prevail.
最高人民法院关于严格规范民商事案件延长审限和延期开庭问题的规定 法释[2018]9号
《最高人民法院关于严格规范民商事案件延长审限和延期开庭问题的规定》已于2018年4月23日由最高人民法院审判委员会第1737次会议通过,现予公布,自2018年4月26日起施行。
二○一八年四月二十三日
最高人民法院关于严格规范民商事案件
延长审限和延期开庭问题的规定
(2018年4月23日最高人民法院审判委员会第1737次会议通过,自2018年4月26日起施行)
为维护诉讼当事人合法权益,根据《中华人民共和国民事诉讼法》等规定,结合审判实际,现就民商事案件延长审限和延期开庭的有关问题规定如下。
第一条
法律规定有特殊情况需要延长审限的,独任审判员或合议庭应当在期限届满十五日前向本院院长提出申请,并说明详细情况和理由。院长应当在期限届满五日前作出决定。
经本院院长批准延长审限后尚不能结案,需要再次延长的,应当在期限届满十五日前报请上级人民法院批准。上级人民法院应当在审限届满五日前作出决定。
第二条
第三条
第四条
第五条
第六条 本规定自2018年4月26日起施行;最高人民法院此前发布的司法解释及规范性文件与本规定不一致的,以本规定为准。
Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Strictly Regulating the Extension of Trial Term and the Postponement of Hearing of Civil and Commercial Cases Interpretation No. 9 [2018] of the Supreme People's Court
The Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Strictly Regulating the Extension of Trial Term and the Postponement of Hearing of Civil and Commercial Cases, which were adopted at the 1737th Session of the Judicial Committee of the Supreme People’s Court on April 23, 2018, are hereby promulgated and shall take effect as of April 26, 2018.
April 23, 2018
Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on Issues concerning Strictly
Regulating the Extension of Trial Term and the Postponement of Hearing of Civil and Commercial Cases
(Adopted at the 1737th Session of the Judicial Committee of the Supreme People’s Court on April 23, 2018, and effective as of April 26, 2018)
To safeguard legitimate rights and interests of litigants, the following Regulations on issues concerning the extension of trial term and the postponement of hearing of civil and commercial cases are issued pursuant to the Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China, etc., combined with practical work of the people's court.
Article 1 A people’s court shall strictly abide by Regulations of laws and judicial interpretations concerning trial term when hearing civil and commercial cases. For cases of first instance to which ordinary procedure is applied, the trial term shall be six months; for cases of first instance to which simple procedure is applied, the trial term shall be three months. Where a people’s court adjudicates an appeal from a judgment, the trial term shall be three months; where a people’s court adjudicates an appeal from a ruling, the trial term shall be thirty days.
Where any extension of the trial term is necessitated by special circumstances as stipulated by laws, the sole judge or collegial panel shall apply to the president of the Court fifteen days before expiration of the term, and present detailed information and reasons. The president shall make decision five days before expiration of the term.
Where the case can’t be closed after the president of the Court has approved to extend the trial term, any further extension if needed shall be reported to the people’s court at a higher level for approval. The people’s court at a higher level shall make decision five days before expiration of the trial term.
Article 2 Where a people’s court deems it necessary to hold a second hearing after opening court sessions of civil and commercial cases, the people’s court shall notify the parties involved of the next hearing date according to law. Interval between two court dates shall be no more than one month, except for force majeure or except as otherwise agreed by the parties involved.
Article 3 Where the sole judge or collegial panel decides to postpone a hearing by referring to Regulations of Article 146.4 of the Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China, the sole judge or collegial panel shall report to the president of the Court for approval.
Article 4 A people’s court shall timely publicize a case’s filing time, trial term, deduction, extension and recalculation of trial term, and particulars and causes for postponement of hearing, to the parties involved and their statutory agent and agent ad litem in accordance with the Regulations of the Supreme People’s Court on a People’s Court Publicizing Adjudication Procedure Information through the Internet. Where the parties involved and their statutory agent and agent ad litem have any objection, they may apply to the court seized of the case for supervision.
Article 5 Where any delay in handling a case for deliberate violation of laws, adjudication disciplines and adjudication management Regulations or for negligence has caused serious consequences, punishment shall be imposed in accordance with Article 47 of the Punishment Ordinance for the Personnel Working in People’s Courts.
Article 6 These Regulations shall take effect as of April 26, 2018; in the event of any discrepancy between judicial interpretations and normative documents previously promulgated by the Supreme People’s Court and these Regulations, the Regulations shall prevail.
最高人民法院印发 《全国法院破产审判工作会议纪要》的通知
各省、自治区、直辖市高级人民法院,解放军军事法院,新疆维吾尔自治区高级人民法院生产建设兵团分院:
现将《全国法院破产审判工作会议纪要》印发给你们,请认真遵照执行。
最高人民法院
2018年3月4日
全国法院破产审判工作会议纪要
为落实党的十九大报告提出的贯彻新发展理念、建设现代化经济体系的要求,紧紧围绕高质量发展这条主线,服务和保障供给侧结构性改革,充分发挥人民法院破产审判工作在完善社会主义市场经济主体拯救和退出机制中的积极作用,为决胜全面建成小康社会提供更加有力的司法保障,2017年12月25日,最高人民法院在广东省深圳市召开了全国法院破产审判工作会议。各省、自治区、直辖市高级人民法院、设立破产审判庭的市中级人民法院的代表参加了会议。与会代表经认真讨论,对人民法院破产审判涉及的主要问题达成共识。现纪要如下:
一、破产审判的总体要求
会议认为,人民法院要坚持以习近平新时代中国特色社会主义经济思想为指导,深刻认识破产法治对决胜全面建成小康社会的重要意义,以更加有力的举措开展破产审判工作,为经济社会持续健康发展提供更加有力的司法保障。当前和今后一个时期,破产审判工作总的要求是:
一要发挥破产审判功能,助推建设现代化经济体系。人民法院要通过破产工作实现资源重新配置,用好企业破产中权益、经营管理、资产、技术等重大调整的有利契机,对不同企业分类处置,把科技、资本、劳动力和人力资源等生产要素调动好、配置好、协同好,促进实体经济和产业体系优质高效。
二要着力服务构建新的经济体制,完善市场主体救治和退出机制。要充分运用重整、和解法律手段实现市场主体的有效救治,帮助企业提质增效;运用清算手段促使丧失经营价值的企业和产能及时退出市场,实现优胜劣汰,从而完善社会主义市场主体的救治和退出机制。
三要健全破产审判工作机制,最大限度释放破产审判的价值。要进一步完善破产重整企业识别、政府与法院协调、案件信息沟通、合法有序的利益衡平四项破产审判工作机制,推动破产审判工作良性运行,彰显破产审判工作的制度价值和社会责任。
四要完善执行与破产工作的有序衔接,推动解决“执行难”。要将破产审判作为与立案、审判、执行既相互衔接、又相对独立的一个重要环节,充分发挥破产审判对化解执行积案的促进功能,消除执行转破产的障碍,从司法工作机制上探索解决“执行难”的有效途径。
二、破产审判的专业化建设
审判专业化是破产审判工作取得实质性进展的关键环节。各级法院要大力加强破产审判专业化建设,努力实现审判机构专业化、审判队伍专业化、审判程序规范化、裁判规则标准化、绩效考评科学化。
1.推进破产审判机构专业化建设。省会城市、副省级城市所在地中级人民法院要根据最高人民法院《关于在中级人民法院设立清算与破产审判庭的工作方案》(法〔2016〕209号),抓紧设立清算与破产审判庭。其他各级法院可根据本地工作实际需求决定设立清算与破产审判庭或专门的合议庭,培养熟悉清算与破产审判的专业法官,以适应破产审判工作的需求。
2.合理配置审判任务。要根据破产案件数量、案件难易程度、审判力量等情况,合理分配各级法院的审判任务。对于债权债务关系复杂、审理难度大的破产案件,高级人民法院可以探索实行中级人民法院集中管辖为原则、基层人民法院管辖为例外的管辖制度;对于债权债务关系简单、审理难度不大的破产案件,可以主要由基层人民法院管辖,通过快速审理程序高效审结。
3.建立科学的绩效考评体系。 要尽快完善清算与破产审判工作绩效考评体系,在充分尊重司法规律的基础上确定绩效考评标准,避免将办理清算破产案件与普通案件简单对比、等量齐观、同等考核。
三、管理人制度的完善
管理人是破产程序的主要推动者和破产事务的具体执行者。管理人的能力和素质不仅影响破产审判工作的质量,还关系到破产企业的命运与未来发展。要加快完善管理人制度,大力提升管理人职业素养和执业能力,强化对管理人的履职保障和有效监督,为改善企业经营、优化产业结构提供有力制度保障。
4.完善管理人队伍结构。人民法院要指导编入管理人名册的中介机构采取适当方式吸收具有专业技术知识、企业经营能力的人员充实到管理人队伍中来,促进管理人队伍内在结构更加合理,充分发挥和提升管理人在企业病因诊断、资源整合等方面的重要作用。
5.探索管理人跨区域执业。除从本地名册选择管理人外,各地法院还可以探索从外省、市管理人名册中选任管理人,确保重大破产案件能够遴选出最佳管理人。两家以上具备资质的中介机构请求联合担任同一破产案件管理人的,人民法院经审查符合自愿协商、优势互补、权责一致要求且确有必要的,可以准许。
6.实行管理人分级管理。高级人民法院或者自行编制管理人名册的中级人民法院可以综合考虑管理人的专业水准、工作经验、执业操守、工作绩效、勤勉程度等因素,合理确定管理人等级,对管理人实行分级管理、定期考评。对债务人财产数量不多、债权债务关系简单的破产案件,可以在相应等级的管理人中采取轮候、抽签、摇号等随机方式指定管理人。
7.建立竞争选定管理人工作机制。破产案件中可以引入竞争机制选任管理人,提升破产管理质量。上市公司破产案件、在本地有重大影响的破产案件或者债权债务关系复杂,涉及债权人、职工以及利害关系人人数较多的破产案件,在指定管理人时,一般应当通过竞争方式依法选定。
8. 合理划分法院和管理人的职能范围。人民法院应当支持和保障管理人依法履行职责,不得代替管理人作出本应由管理人自己作出的决定。管理人应当依法管理和处分债务人财产,审慎决定债务人内部管理事务,不得将自己的职责全部或者部分转让给他人。
9.进一步落实管理人职责。在债务人自行管理的重整程序中,人民法院要督促管理人制订监督债务人的具体制度。在重整计划规定的监督期内,管理人应当代表债务人参加监督期开始前已经启动而尚未终结的诉讼、仲裁活动。重整程序、和解程序转入破产清算程序后,管理人应当按照破产清算程序继续履行管理人职责。
10.发挥管理人报酬的激励和约束作用。人民法院可以根据破产案件的不同情况确定管理人报酬的支付方式,发挥管理人报酬在激励、约束管理人勤勉履职方面的积极作用。管理人报酬原则上应当根据破产案件审理进度和管理人履职情况分期支付。案情简单、耗时较短的破产案件,可以在破产程序终结后一次性向管理人支付报酬。
11.管理人聘用其他人员费用负担的规制。管理人经人民法院许可聘用企业经营管理人员,或者管理人确有必要聘请其他社会中介机构或人员处理重大诉讼、仲裁、执行或审计等专业性较强工作,如所需费用需要列入破产费用的,应当经债权人会议同意。
12.推动建立破产费用的综合保障制度。各地法院要积极争取财政部门支持,或采取从其他破产案件管理人报酬中提取一定比例等方式,推动设立破产费用保障资金,建立破产费用保障长效机制,解决因债务人财产不足以支付破产费用而影响破产程序启动的问题。
13.支持和引导成立管理人协会。人民法院应当支持、引导、推动本辖区范围内管理人名册中的社会中介机构、个人成立管理人协会,加强对管理人的管理和约束,维护管理人的合法权益,逐步形成规范、稳定和自律的行业组织,确保管理人队伍既充满活力又规范有序发展。
四、破产重整
会议认为,重整制度集中体现了破产法的拯救功能,代表了现代破产法的发展趋势,全国各级法院要高度重视重整工作,妥善审理企业重整案件,通过市场化、法治化途径挽救困境企业,不断完善社会主义市场主体救治机制。
14.重整企业的识别审查。破产重整的对象应当是具有挽救价值和可能的困境企业;对于僵尸企业,应通过破产清算,果断实现市场出清。人民法院在审查重整申请时,根据债务人的资产状况、技术工艺、生产销售、行业前景等因素,能够认定债务人明显不具备重整价值以及拯救可能性的,应裁定不予受理。
15.重整案件的听证程序。对于债权债务关系复杂、债务规模较大,或者涉及上市公司重整的案件,人民法院在审查重整申请时,可以组织申请人、被申请人听证。债权人、出资人、重整投资人等利害关系人经人民法院准许,也可以参加听证。听证期间不计入重整申请审查期限。
16.重整计划的制定及沟通协调。人民法院要加强与管理人或债务人的沟通,引导其分析债务人陷于困境的原因,有针对性地制定重整计划草案,促使企业重新获得盈利能力,提高重整成功率。人民法院要与政府建立沟通协调机制,帮助管理人或债务人解决重整计划草案制定中的困难和问题。
17.重整计划的审查与批准。重整不限于债务减免和财务调整,重整的重点是维持企业的营运价值。人民法院在审查重整计划时,除合法性审查外,还应审查其中的经营方案是否具有可行性。重整计划中关于企业重新获得盈利能力的经营方案具有可行性、表决程序合法、内容不损害各表决组中反对者的清偿利益的,人民法院应当自收到申请之日起三十日内裁定批准重整计划。
18.重整计划草案强制批准的条件。人民法院应当审慎适用企业破产法第八十七条第二款,不得滥用强制批准权。确需强制批准重整计划草案的,重整计划草案除应当符合企业破产法第八十七条第二款规定外,如债权人分多组的,还应当至少有一组已经通过重整计划草案,且各表决组中反对者能够获得的清偿利益不低于依照破产清算程序所能获得的利益。
19.重整计划执行中的变更条件和程序。债务人应严格执行重整计划,但因出现国家政策调整、法律修改变化等特殊情况,导致原重整计划无法执行的,债务人或管理人可以申请变更重整计划一次。债权人会议决议同意变更重整计划的,应自决议通过之日起十日内提请人民法院批准。债权人会议决议不同意或者人民法院不批准变更申请的,人民法院经管理人或者利害关系人请求,应当裁定终止重整计划的执行,并宣告债务人破产。
20.重整计划变更后的重新表决与裁定批准。人民法院裁定同意变更重整计划的,债务人或者管理人应当在六个月内提出新的重整计划。变更后的重整计划应提交给因重整计划变更而遭受不利影响的债权人组和出资人组进行表决。表决、申请人民法院批准以及人民法院裁定是否批准的程序与原重整计划的相同。
21.重整后企业正常生产经营的保障。企业重整后,投资主体、股权结构、公司治理模式、经营方式等与原企业相比,往往发生了根本变化,人民法院要通过加强与政府的沟通协调,帮助重整企业修复信用记录,依法获取税收优惠,以利于重整企业恢复正常生产经营。
22.探索推行庭外重组与庭内重整制度的衔接。在企业进入重整程序之前,可以先由债权人与债务人、出资人等利害关系人通过庭外商业谈判,拟定重组方案。重整程序启动后,可以重组方案为依据拟定重整计划草案提交人民法院依法审查批准。
五、破产清算
会议认为,破产清算作为破产制度的重要组成部分,具有淘汰落后产能、优化市场资源配置的直接作用。对于缺乏拯救价值和可能性的债务人,要及时通过破产清算程序对债权债务关系进行全面清理,重新配置社会资源,提升社会有效供给的质量和水平,增强企业破产法对市场经济发展的引领作用。
23.破产宣告的条件。人民法院受理破产清算申请后,第一次债权人会议上无人提出重整或和解申请的,管理人应当在债权审核确认和必要的审计、资产评估后,及时向人民法院提出宣告破产的申请。人民法院受理破产和解或重整申请后,债务人出现应当宣告破产的法定原因时,人民法院应当依法宣告债务人破产。
24.破产宣告的程序及转换限制。相关主体向人民法院提出宣告破产申请的,人民法院应当自收到申请之日起七日内作出破产宣告裁定并进行公告。债务人被宣告破产后,不得再转入重整程序或和解程序。
25.担保权人权利的行使与限制。在破产清算和破产和解程序中,对债务人特定财产享有担保权的债权人可以随时向管理人主张就该特定财产变价处置行使优先受偿权,管理人应及时变价处置,不得以须经债权人会议决议等为由拒绝。但因单独处置担保财产会降低其他破产财产的价值而应整体处置的除外。
26.破产财产的处置。破产财产处置应当以价值最大化为原则,兼顾处置效率。人民法院要积极探索更为有效的破产财产处置方式和渠道,最大限度提升破产财产变价率。采用拍卖方式进行处置的,拍卖所得预计不足以支付评估拍卖费用,或者拍卖不成的,经债权人会议决议,可以采取作价变卖或实物分配方式。变卖或实物分配的方案经债权人会议两次表决仍未通过的,由人民法院裁定处理。
27.企业破产与职工权益保护。破产程序中要依法妥善处理劳动关系,推动完善职工欠薪保障机制,依法保护职工生存权。由第三方垫付的职工债权,原则上按照垫付的职工债权性质进行清偿;由欠薪保障基金垫付的,应按照企业破产法第一百一十三条第一款第二项的顺序清偿。债务人欠缴的住房公积金,按照债务人拖欠的职工工资性质清偿。
28.破产债权的清偿原则和顺序。对于法律没有明确规定清偿顺序的债权,人民法院可以按照人身损害赔偿债权优先于财产性债权、私法债权优先于公法债权、补偿性债权优先于惩罚性债权的原则合理确定清偿顺序。因债务人侵权行为造成的人身损害赔偿,可以参照企业破产法第一百一十三条第一款第一项规定的顺序清偿,但其中涉及的惩罚性赔偿除外。破产财产依照企业破产法第一百一十三条规定的顺序清偿后仍有剩余的,可依次用于清偿破产受理前产生的民事惩罚性赔偿金、行政罚款、刑事罚金等惩罚性债权。
29.建立破产案件审理的繁简分流机制。人民法院审理破产案件应当提升审判效率,在确保利害关系人程序和实体权利不受损害的前提下,建立破产案件审理的繁简分流机制。对于债权债务关系明确、债务人财产状况清楚的破产案件,可以通过缩短程序时间、简化流程等方式加快案件审理进程,但不得突破法律规定的最低期限。
30.破产清算程序的终结。人民法院终结破产清算程序应当以查明债务人财产状况、明确债务人财产的分配方案、确保破产债权获得依法清偿为基础。破产申请受理后,经管理人调查,债务人财产不足以清偿破产费用且无人代为清偿或垫付的,人民法院应当依管理人申请宣告破产并裁定终结破产清算程序。
31.保证人的清偿责任和求偿权的限制。破产程序终结前,已向债权人承担了保证责任的保证人,可以要求债务人向其转付已申报债权的债权人在破产程序中应得清偿部分。破产程序终结后,债权人就破产程序中未受清偿部分要求保证人承担保证责任的,应在破产程序终结后六个月内提出。保证人承担保证责任后,不得再向和解或重整后的债务人行使求偿权。
六、关联企业破产
会议认为,人民法院审理关联企业破产案件时,要立足于破产关联企业之间的具体关系模式,采取不同方式予以处理。既要通过实质合并审理方式处理法人人格高度混同的关联关系,确保全体债权人公平清偿,也要避免不当采用实质合并审理方式损害相关利益主体的合法权益。
32.关联企业实质合并破产的审慎适用。人民法院在审理企业破产案件时,应当尊重企业法人人格的独立性,以对关联企业成员的破产原因进行单独判断并适用单个破产程序为基本原则。当关联企业成员之间存在法人人格高度混同、区分各关联企业成员财产的成本过高、严重损害债权人公平清偿利益时,可例外适用关联企业实质合并破产方式进行审理。
33.实质合并申请的审查。人民法院收到实质合并申请后,应当及时通知相关利害关系人并组织听证,听证时间不计入审查时间。人民法院在审查实质合并申请过程中,可以综合考虑关联企业之间资产的混同程序及其持续时间、各企业之间的利益关系、债权人整体清偿利益、增加企业重整的可能性等因素,在收到申请之日起三十日内作出是否实质合并审理的裁定。
34.裁定实质合并时利害关系人的权利救济。相关利害关系人对受理法院作出的实质合并审理裁定不服的,可以自裁定书送达之日起十五日内向受理法院的上一级人民法院申请复议。
35.实质合并审理的管辖原则与冲突解决。采用实质合并方式审理关联企业破产案件的,应由关联企业中的核心控制企业住所地人民法院管辖。核心控制企业不明确的,由关联企业主要财产所在地人民法院管辖。多个法院之间对管辖权发生争议的,应当报请共同的上级人民法院指定管辖。
36.实质合并审理的法律后果。人民法院裁定采用实质合并方式审理破产案件的,各关联企业成员之间的债权债务归于消灭,各成员的财产作为合并后统一的破产财产,由各成员的债权人在同一程序中按照法定顺序公平受偿。采用实质合并方式进行重整的,重整计划草案中应当制定统一的债权分类、债权调整和债权受偿方案。
37.实质合并审理后的企业成员存续。适用实质合并规则进行破产清算的,破产程序终结后各关联企业成员均应予以注销。适用实质合并规则进行和解或重整的,各关联企业原则上应当合并为一个企业。根据和解协议或重整计划,确有需要保持个别企业独立的,应当依照企业分立的有关规则单独处理。
38.关联企业破产案件的协调审理与管辖原则。多个关联企业成员均存在破产原因但不符合实质合并条件的,人民法院可根据相关主体的申请对多个破产程序进行协调审理,并可根据程序协调的需要,综合考虑破产案件审理的效率、破产申请的先后顺序、成员负债规模大小、核心控制企业住所地等因素,由共同的上级法院确定一家法院集中管辖。
39.协调审理的法律后果。协调审理不消灭关联企业成员之间的债权债务关系,不对关联企业成员的财产进行合并,各关联企业成员的债权人仍以该企业成员财产为限依法获得清偿。但关联企业成员之间不当利用关联关系形成的债权,应当劣后于其他普通债权顺序清偿,且该劣后债权人不得就其他关联企业成员提供的特定财产优先受偿。
七、执行程序与破产程序的衔接
执行程序与破产程序的有效衔接是全面推进破产审判工作的有力抓手,也是破解“执行难”的重要举措。全国各级法院要深刻认识执行转破产工作的重要意义,大力推动符合破产条件的执行案件,包括执行不能案件进入破产程序,充分发挥破产程序的制度价值。
40.执行法院的审查告知、释明义务和移送职责。执行部门要高度重视执行与破产的衔接工作,推动符合条件的执行案件向破产程序移转。执行法院发现作为被执行人的企业法人符合企业破产法第二条规定的,应当及时询问当事人是否同意将案件移送破产审查并释明法律后果。执行法院作出移送决定后,应当书面通知所有已知执行法院,执行法院均应中止对被执行人的执行程序。
41.执行转破产案件的移送和接收。执行法院与受移送法院应加强移送环节的协调配合,提升工作实效。执行法院移送案件时,应当确保材料完备,内容、形式符合规定。受移送法院应当认真审核并及时反馈意见,不得无故不予接收或暂缓立案。
42.破产案件受理后查封措施的解除或查封财产的移送。执行法院收到破产受理裁定后,应当解除对债务人财产的查封、扣押、冻结措施;或者根据破产受理法院的要求,出具函件将查封、扣押、冻结财产的处置权交破产受理法院。破产受理法院可以持执行法院的移送处置函件进行续行查封、扣押、冻结,解除查封、扣押、冻结,或者予以处置。
执行法院收到破产受理裁定拒不解除查封、扣押、冻结措施的,破产受理法院可以请求执行法院的上级法院依法予以纠正。
43.破产审判部门与执行部门的信息共享。破产受理法院可以利用执行查控系统查控债务人财产,提高破产审判工作效率,执行部门应予以配合。
各地法院要树立线上线下法律程序同步化的观念,逐步实现符合移送条件的执行案件网上移送,提升移送工作的透明度,提高案件移送、通知、送达、沟通协调等相关工作的效率。
44.强化执行转破产工作的考核与管理。各级法院要结合工作实际建立执行转破产工作考核机制,科学设置考核指标,推动执行转破产工作开展。对应当征询当事人意见不征询、应当提交移送审查不提交、受移送法院违反相关规定拒不接收执行转破产材料或者拒绝立案的,除应当纳入绩效考核和业绩考评体系外,还应当公开通报和严肃追究相关人员的责任。
八、破产信息化建设
会议认为,全国法院要进一步加强破产审判的信息化建设,提升破产案件审理的透明度和公信力,增进破产案件审理质效,促进企业重整再生。
45.充分发挥破产重整案件信息平台对破产审判工作的推动作用。各级法院要按照最高人民法院相关规定,通过破产重整案件信息平台规范破产案件审理,全程公开、步步留痕。要进一步强化信息网的数据统计、数据检索等功能,分析研判企业破产案件情况,及时发现新情况,解决新问题,提升破产案件审判水平。
46.不断加大破产重整案件的信息公开力度。要增加对债务人企业信息的公开内容,吸引潜在投资者,促进资本、技术、管理能力等要素自由流动和有效配置,帮助企业重整再生。要确保债权人等利害关系人及时、充分了解案件进程和债务人相关财务、重整计划草案、重整计划执行等情况,维护债权人等利害关系人的知情权、程序参与权。
47.运用信息化手段提高破产案件处理的质量与效率。要适应信息化发展趋势,积极引导以网络拍卖方式处置破产财产,提升破产财产处置效益。鼓励和规范通过网络方式召开债权人会议,提高效率,降低破产费用,确保债权人等主体参与破产程序的权利。
48.进一步发挥人民法院破产重整案件信息网的枢纽作用。要不断完善和推广使用破产重整案件信息网,在确保增量数据及时录入信息网的同时,加快填充有关存量数据,确立信息网在企业破产大数据方面的枢纽地位,发挥信息网的宣传、交流功能,扩大各方运用信息网的积极性。
九、跨境破产
49.对跨境破产与互惠原则。人民法院在处理跨境破产案件时,要妥善解决跨境破产中的法律冲突与矛盾,合理确定跨境破产案件中的管辖权。在坚持同类债权平等保护的原则下,协调好外国债权人利益与我国债权人利益的平衡,合理保护我国境内职工债权、税收债权等优先权的清偿利益。积极参与、推动跨境破产国际条约的协商与签订,探索互惠原则适用的新方式,加强我国法院和管理人在跨境破产领域的合作,推进国际投资健康有序发展。
50.跨境破产案件中的权利保护与利益平衡。依照企业破产法第五条的规定,开展跨境破产协作。人民法院认可外国法院作出的破产案件的判决、裁定后,债务人在中华人民共和国境内的财产在全额清偿境内的担保权人、职工债权和社会保险费用、所欠税款等优先权后,剩余财产可以按照该外国法院的规定进行分配。
Notice of the Supreme People's Court on the Minutes of National Court Bankruptcy Trial Meeting
High People's Courts of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government, military courts of the People's Liberation Army, branch of the Production and Construction Corps of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region High People's Court:
TheMinutes of National Court Bankruptcy Trial Meeting is hereby printed and distributed to you. Please follow them carefully.
Supreme People's Court
March 4, 2018
Minutes of National Court Bankruptcy Trial Meeting
In order to fulfill the requirements of implementing the new development concept and building a modern economic system put forward by the Party's Nineteenth Congress report, we will closely focus on the main line of high-quality development, serve and guarantee structural reforms on the supply side, and give full play to the positive role of the bankruptcy trial work of the people's court on the rescue and withdrawal mechanism of improving socialist market economy entities, provide a more powerful judicial guarantee for the success of a well-off society. On December 25, 2017, the Supreme People's Court held a national court bankruptcy trial meeting in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province. Representatives of the High People's Courts of provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government and the Municipal Intermediate People's Court with the Bankruptcy Trial Division attended the meeting. After a serious discussion, the delegates reached a consensus on the main issues involved in the bankruptcy trial of the people's court. The minutes are as follows:
I. General requirements of thebankruptcytrial
The meeting held that the people's courts must adhere to the guidance of the socialist economic ideology with Chinese characteristics in the new era of Xi Jinping and profoundly understand the importance of bankruptcy law in building a well-off society. The bankruptcy trials should be conducted with more powerful measures to provide more powerful judicial guarantees for ensuring a sustained and healthy economic and social development. At present time and for a period to come, the general requirements for bankruptcy trials are:
First, we must use the bankruptcy trial function to boost the construction of a modern economic system. The people’s courts need to reallocate resources through bankruptcy work, make good use of the favorable opportunities of major adjustments in corporate bankruptcy such as rights and interests, operation management, assets, and technology to dispose of different types of businesses and mobilize, configure and coordinate production factors well such as science and technology, capital, labor, and human resources so as to promote the quality and efficiency of the real economy and industrial system.
Second, we must focus on services to build a new economic system and improve the mechanism for the rescue and withdrawal of market entities. It is necessary to make full use of reorganization and reconciliation laws to achieve effective treatment of market entities and help enterprises improve quality and efficiency; use liquidation methods to prompt enterprises and production capacity that have lost business value to withdraw from the market in a timely manner to achieve survival of the fittest, thereby improving the rescue and withdrawal mechanism of socialist market entities.
Third, we must improve the working mechanism of bankruptcy trials and maximize the value of bankruptcy trials. It is necessary to further improve the recognition of the four bankruptcy trial working mechanisms, including bankruptcy reorganization of corporate identity, the coordination of government and courts, the communication of case information, and the lawful and orderly interests balance, promote the sound operation of bankruptcy trials, and highlight the institutional value and social responsibility of bankruptcy trial work.
Fourth, we must improve the orderly connection between implementation and bankruptcy, and promote the resolution of “Law enforcement difficulty”. Bankruptcy trials should be used as an important link with filing, trial, and execution, which are both mutually connected and relatively independent. The promotion function of bankruptcy trials to resolve accumulated cases should be brought into full play, and the obstacles to the implementation of bankruptcy transfers should be eliminated. The judicial work mechanism should be used to explore the effective ways to solve “law enforcement difficulty”.
II. Professionalization of bankruptcy trials
The professionalization of trials is the key link for substantial progress in the bankruptcy trial. Courts at all levels must vigorously strengthen the professionalization of bankruptcy trials and strive to achieve the professionalization of trial institutions, the professionalization of trial teams, the normalization of trial procedures, the standardization of referee rules, and the scientization of performance appraisal.
1. Promote the professionalization of bankruptcy trial institutions. The intermediate people's courts of the provincial capital and sub-provincial cities shall set up a liquidation and bankruptcy trial court in accordance with the “Work Plan on Establishing a Liquidation and Bankruptcy Trial Division at the Intermediate People's Court” issued by Supreme People's Court (Fa [2016] No. 209). Other courts at all levels may decide to establish a liquidation and bankruptcy trial division or a special collegiate bench based on the actual needs of local work, and to train professional judges who are familiar with liquidation and bankruptcy trials to meet the needs of bankruptcy trials.
2. Reasonably configure the trial mission.The trial tasks of the courts at all levels must be reasonably distributed according to the number of bankruptcy cases, the degree of difficulty of the case, the strength of the trial, etc. For a bankruptcy case with a complicated debt and credit relationship and a difficult trial, the high people's court can explore the jurisdictional system where the principle of centralized jurisdiction of the intermediate people's court is applied and the jurisdiction of the basic people's court is the exception; While the bankruptcy case with a simple debt and credit relationship and less difficult trial can be mainly governed by the basic people's court, and it can be concluded through high-speed trial procedures.
3. Establish a scientific performance evaluation system.It is necessary to improve the performance evaluation system for liquidation and bankruptcy trials as soon as possible, determine performance evaluation criteria on the basis of full respect for the law of the judiciary, and avoid the simple comparison of liquidation and bankruptcy cases with ordinary cases, and avoid equating and assess them equally.
III. Improvement of the administrator system
The administrator is the main promoter of the bankruptcy proceedings and the concrete executor of the bankruptcy affairs. The administrator's ability and quality not only affect the quality of the bankruptcy trial, but also affect the fate and future development of the bankrupt enterprise. It is necessary to speed up the improvement of the administrator system, vigorously enhance the administrator's professional quality and operation ability, strengthen the duty performance guarantee and effective supervision for administrators, and provide a strong institutional guarantee for the improvement of business operations and optimization of the industrial structure.
4. Improve the administrator team structure. The people's courts shall instruct the intermediary institutions who incorporated in the register of administrators to adopt appropriate methods to recruit professionals with professional technical knowledge and business operation capabilities to the administrator team, and to promote the internal structure of the managerial team to be more reasonable, and to give full play and enhance the important role of administrators in enterprise etiology diagnosis, resource integration and other important aspects.
5. Explore administrators' practice across regions. In addition to selecting administrators from the local roster, local courts can also try to select administrators from the list of provincial and municipal administrators to ensure that they can select the best administrators in the major bankruptcy cases. When two or more qualified intermediary agencies request to jointly serve as the administrators of the same bankruptcy case, the people's courts may permit if they meet the requirements of voluntary negotiation, complementing each other, and having consistent requirements of powers and responsibilities.
6. Implement administrator's classification management. A high people’s court or an intermediate people’s court that has compiled its own register of administrators may comprehensively consider the administrator’s professional standards, work experience, professional ethics, work performance, degree of diligence, and other factors, and reasonably determine the level of the administrators, and implement hierarchical management and regular evaluation of the managers. A bankruptcy case with a small number of debtor assets and a simple debtor-creditor relationship may be designated to the administrator at a corresponding level of by waiting, drawing lots or lottery.
7. Establish competitive working mechanism to select the administrators. In a bankruptcy case, a competitive mechanism can be introduced to select administrators and improve the quality of bankruptcy management. The bankruptcy cases of listed companies, bankruptcy cases that have significant local influence, or complex debtor-creditor relationship, bankruptcy cases involving a large number of creditors, employees, and interested parties should generally select administrators through competition, according to law when designating a administrator.
8. Reasonably divide the function scopes of the court and the administrator. The people's court shall support and guarantee that the administrators shall perform their duties in accordance with the law, and shall not take the place of the administrators to make decisions that should have been made by the administrators themselves. The administrators shall manage and dispose of the debtor’s property in accordance with the law, determine the internal management of the debtor in a prudent manner, and may not assign all or part of their duties to others.
9. Further implement administrator’s duties. In the reorganization process that the debtor manages on its own, the people's court must urge the administrator to formulate a specific system for the supervision of the debtor. During the supervision period stipulated in the reorganization plan, the administrator shall represent the debtor in the litigation and arbitration activities that have been started before the start of the supervision period and have not yet been concluded. After the reorganization and reconciliation procedures are transferred to the bankruptcy liquidation procedures, the administrator shall continue to perform the duties of the administrator in accordance with the bankruptcy liquidation procedures.
10. Exert incentive and binding functions of administrators' remuneration. The people's court may determine the payment method of the remuneration of the administrator according to the different circumstances of the bankruptcy cases, and exert the active role of the remuneration of the administrator in motivating and restraining the administrator in performing its duties diligently. The remuneration of the administrator shall, in principle, be paid in installments according to the examination progress of the bankruptcy case and the performance of the administrator. The administrator can be paid once after the bankruptcy proceedings are terminated when the bankruptcy case is simple and consumes short time.
11. Regulations on governing the cost of employing other personnel by administrators. When the administrator employs the business management personnel with the permission of the people's court, or when the administrator really needs to employ other social intermediary agencies or personnel to deal with the professional work such as major lawsuit, arbitration, execution or auditing, if the required expenses need to be included in the bankruptcy expenses, it should be approved by the creditors' meeting.
12. Promote the establishment of a comprehensive security system for bankruptcy expenses. The local courts must actively seek the support of the financial department or take certain proportions from the remunerations of other administrators, promote the establishment of bankruptcy expense protection funds, establish a long-term mechanism for the protection of bankruptcy expenses, and solve the problem that debtor’s assets are insufficient to meet bankruptcy expenses, which affects the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings.
13. Support and guide the establishment of an administrator association. The people's courts shall support, guide, and promote social intermediary agencies and individuals in the list of administrators within their respective jurisdictions to establish administrator associations, strengthen the management and restraint of the administrators, and safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of the administrators, and gradually form normative, stable, and self-disciplined industry organization, and ensures that the administrator team is full of vigor and carry out standardized and orderly development.
IV. Bankruptcy reorganization
The meeting held that the reorganization system embodies the rescue function of the bankruptcy law and represents the development trend of the modern bankruptcy law. The courts at all levels in the country must attach great importance to reorganization work, properly review corporate reorganization cases, and rescue distressed companies through marketization and legalization, constantly improve the rescuing mechanism of the main body of the socialist market.
14. Recognize the recognition and review of the company. The object of bankruptcy reorganization should be a company with rescuing value and possible distressed companies; for zombie enterprises, they should go through bankruptcy liquidation and resolutely achieve market clearing. When reviewing a reorganization application, the people's court shall not accept the application when they think the debtor does not have the reorganization value and the rescuing possibility based on factors such as the debtor’s asset status, technical process, production and sales and industry prospects.
15. Reform the hearing process of the case. For cases involving complicated credits and debts, large scale of the debts, or cases involving the reorganization of listed companies, the people's courts may organize the applicant and the respondent to participate in the hearing when reviewing the application for reorganization. Creditors, investors, restructured investors, and other stakeholders may also participate in the hearing if they are permitted by the people's courts. The hearing period is not included in the reorganization application review period.
16. The formulation and coordination of the reorganization plan. The people's courts must strengthen communication withadministrators or debtors, and guide them to analyze the causes of the debtors’ dilemmas. They must formulate drafts of reorganization plans in a targeted manner to encourage enterprises to regain profitability and increase the success rate of reorganization. The people's court must establish a communication and coordination mechanism with the government to help the administrator or the debtor solve the difficulties and problems in the drafting of the reorganization plan.
17. Review and approval of the reorganization plan. Reorganization is not limited to debt relief and financial adjustments. The focus of reorganization is to maintain the operational value of the company. In reviewing the reorganization plan, the people's courts shall not only review legality, but also review whether the business plan is feasible. If the business plan for regaining profitability of the enterprise in the reorganization plan is feasible, the voting procedure is legal, and the content does not impair the settlement benefit of the opponents in eachvoting group, the people’s court shall order approval of the reorganization plan within thirty days from the date of receipt of the application.
18. The conditions for the compulsory approval of the reorganization plan draft. The people's courts should prudently apply the second paragraph of Article 87 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law and must not abuse the right of compulsory approval. If it is really necessary to compel approval of the draft of the reorganization plan, the draft of the reorganization plan shall comply with the second paragraph of Article 87 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law. If there are more than one group of creditors, at least one group has already passed the draft of the reorganization plan. And the liquidation benefit that opponents in each voting group can obtain is not less than the benefit that can be obtained according to the bankruptcy liquidation procedure.
19. Changeable conditions and procedures for the execution of the reorganization plan. Debtors should strictly implement the reorganization plan, but if the special circumstances occur, such as national policy revision, law revision and other changes, which leads that the original reorganization plan can not be implemented, the debtor or the administrator may apply for changes of the reorganization plan once. If the resolution of the creditors’ meeting agrees to change the reorganization plan, it shall be submitted to the people’s court for approval within ten days from the date of passing the resolution. If the resolution of the creditors’ meeting disagrees or the people’s court does not approve the application for change, the people’s court shall, upon the request of the administrator or an interested person, decide to terminate the implementation of the reorganization plan and declare the debtor bankrupt.
20. The re-voting and ruling approval after the change of the reorganization plan. When the people's court agrees to change the reorganization plan, the debtor or the administrator shall propose a new reorganization plan within six months. The changed reorganization plan shall be submitted to the creditor group and the contributor group that have been adversely affected by the change of the reorganization plan. The procedures for voting, applying for approval by the people's court, and whether the people's court rules for approval are the same as those of the original reorganization plan.
21. Guarantee of normal production and business operations after restructuring. After the reorganization of the enterprise, compared with the original enterprise, the investment subject, the ownership structure, the corporate governance model and the business operation often undergo fundamental changes. The people's courts must strengthen the communication and coordination with the government and help the restructured enterprise to repair credit records, get tax incentives so as to help the restructured enterprise to resume normal production and operations.
22. Explore the connection between out-of-court reorganization and in-court reorganization. Before the company enters the reorganization process, creditors, debtors, contributors, and other interested parties may formulate reorganization plans through out-of-court commercial negotiations. After the initiation of the reorganization procedure, the reorganization plan draft may be prepared based on the reorganization plan and submitted to the people's court for review and approval.
V. Bankruptcy liquidation
The meeting held that bankruptcy liquidation, as an important component of the bankruptcy system, has the direct effect of eliminating backward production capacity and optimizing the allocation of market resources. For the debtor who lacks the rescuing value and possibility, it is necessary to timely clear the creditor’s rights and debts through bankruptcy liquidation procedures, reconfigure social resources, improve the quality and level of effective social supply, and strengthen the leading role of the bankruptcy law for market economy development.
23. Conditions for the declaration of bankruptcy. After the people’s court accepts the application for bankruptcy liquidation, and no one proposes a reorganization or settlement application at the first creditors’ meeting, the administrator shall promptly file an application for declaring bankruptcy in the people’s court after the debtor’s right to review and confirm and the necessary auditing and asset assessment. After the people’s court accepts the application for bankruptcy conciliation or reorganization, when the debtor has the legal reason to declare bankruptcy, the people’s court shall declare the debtor bankrupt according to laws.
24. Procedures for the announcement of bankruptcy and restrictions on conversion. Where the relevant entity submits an application for declaring bankruptcy to the people's court, the people's court shall, within seven days from the date of receipt of the application, make a ruling of bankruptcy and make an announcement. After the debtor is declared bankrupt, it may not be transferred to a reorganization procedure or a conciliation procedure.
25. Execution and limitations of the rights of the secured party. In bankruptcy liquidation and bankruptcy reconciliation proceedings, a creditor who has a security right over the debtor’s specific property may at any time submit to the administrator a preferential right of redress for the disposal of the particular property, and the administrator shall promptly change the price, and may not refuse at the reason that it should be resolved at the meeting of the creditor. However, since the disposal of the secured property by itself will reduce the value of other bankruptcy assets, it should be treated as a whole.
26. Disposal of bankruptcy property. Disposal of bankruptcy assets should be based on the principle of maximizing value and giving consideration to disposal efficiency. The people's court must actively explore more effective methods and channels for the disposal of bankruptcy property, and maximize the rate of change of bankruptcy property. If an auction is used for disposal, the proceeds from the auction are not expected to be sufficient to cover the cost of the auction, or if the auction fails, the creditor’s meeting may adopt resolutions to sell or distribute in kind. If the scheme for sale or in-kind distribution has not been approved by the creditors’ meeting twice, it shall be determined by the people’s court.
27. Corporate bankruptcy and the protection of employees’ rights and interests. Bankruptcy procedures should properly handle labor relations according to law, promote the improvement of the wage arrears protection system for workers, and protect the rights of employees to survive in accordance with the law. The employees’ claims advanced by the third party shall, in principle, be repaid in accordance with the nature of the advanced creditor’s claims; Advances made by the wage-insurance fund shall be paid in accordance with the order of the second item of the first paragraph of Article 113 of the Bankruptcy Law. The housing accumulation fund owed by the debtor is repaid in accordance with the nature of the wages owed by the debtor.
28. The principle and sequence of liquidation of bankruptcy claims. For the claims that the law does not clearly stipulate the order of repayment, the people's court may reasonably determine the order of repayment in accordance with the principles of personal injury claims over priority of property claims, private law claims over public law claims, and compensatory claims over punitive claims. The compensation for personal injury caused by the debtor’s infringement can be paid in the order specified in the first item of the first paragraph of Article 113 of the Bankruptcy Law, with the exception of the involved punitive damages. After the bankruptcy property has been repaid in accordance with the order stipulated in Article 113 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, it may still be used to liquidate punitive claims such as civil punitive damages, administrative fines, and criminal fines incurred prior to bankruptcy acceptance.
29. Establish the simple and streamlined mechanism for the hearing of bankruptcy cases. People’s courts should improve trial efficiency of the hearing of bankruptcy cases. Under the premise of ensuring that the procedures and substantive rights of interested parties are not compromised, a simple and streamlined mechanism for hearing bankruptcy cases should be established. For bankruptcy cases where the creditor’s rights and liabilities are clearly defined and the debtor’s property is clearly stated, the process of hearing the case can be expedited by shortening the process time, simplifying the process, etc., but the minimum period prescribed by law may not be exceeded.
30. The end of the bankruptcy liquidation process. The completion of the bankruptcy liquidation procedure by the people's court shall be based on the identification of the debtor’s property status, the clear distribution of the debtor’s property, and the securing of the bankruptcy creditor’s rights according to law. After the bankruptcy application has been accepted, if the debtor’s property is insufficient to pay off the bankruptcy expenses and no one has paid off or advances it upon investigation by the administrator, the people’s court shall declare bankruptcy and order the termination of the bankruptcy liquidation procedure according to the administrator’s application.
31. The guarantor's liability for repayment and the limitation of its right of claim. Before the conclusion of the bankruptcy proceedings, the guarantor who has assumed the guaranty responsibility for the creditor may request the debtor to transfer to pay the portion that should have been paid to the creditor who has declared the creditor’s right in the bankruptcy proceedings. After the conclusion of the bankruptcy proceedings, the creditor shall, within the unclaimed portion of the bankruptcy proceedings, demand the guarantor to assume the guaranty liability, which shall be filed within six months after the conclusion of the bankruptcy proceedings. After the guarantor assumes the responsibility of guarantee, it may not exercise the right of repayment to the debtor after the reconciliation or reorganization.
VI. Bankruptcy of related companies
The meeting held that when people's courts try bankruptcy cases involving affiliated companies, they must base themselves on the specific relationships between bankrupt affiliates and adopt different methods to handle them. It is necessary to deal with the highly confusing relationship of corporate personality by means of substantive merger trials to ensure that all creditors are fairly liquidated and to avoid improper use of substantive merger trials to damage the legitimate rights and interests of relevant stakeholders.
32. The prudent application of related companies’ substantive merger and bankruptcy. When people’s courts try business bankruptcy cases, they should respect the independence of the corporate personality, and make independent judgments on the bankruptcy causes of the members of related companies and apply a single bankruptcy procedure as the basic principle. When there is a high degree of confusion between corporate personality of the members of an related company, the cost of distinguishing each affiliate member’s property is too high, and the creditor’s fair settlement of benefits is seriously impaired, the related companies substantive merger bankruptcy can be used in exceptional cases.
33. Review of the substantive merger application. After receiving the application for substantive merger, the people's court shall promptly notify the relevant stakeholders and organize a hearing. The time for hearing shall not be included in the examination time. In reviewing the substantive merger application process, the people's court may comprehensively consider the factors such as the mixed procedures and duration of assets among related companies, the interest relationships among enterprises, the overall liquidation of creditors, and the possibility of increasing corporate restructuring. The ruling of whether or not to take a substantive joint review should be made within thirty days from the date of receipt of the application.
34. The remedy of the rights of the interested parties in the substantive consolidation. If the relevant interested party is not satisfied with the adjudicative ruling made by the court of admissibility, it may apply for reconsideration from the people's court at the superior level to the admissibility court within fifteen days from the date of the arrival of the written verdict.
35. Jurisdiction principles and conflict resolution in substantive merger trials. When the bankruptcy case of an related company is tried in a substantive merger, it shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court of the affiliated enterprise where the core control enterprise is domiciled. When the core controlling company is not clear, it shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court where the main property of the affiliated company is located. When disputes arise between multiple courts regarding jurisdiction, they shall report to the common superior people's court for determination of jurisdiction.
36. Legal consequences of substantive merger proceedings. When the people’s court rules that the bankruptcy case is to be examined by a substantive merger, the creditor’s rights and debts among the members of the related company shall be extinguished, and the property of each member shall be the unified bankruptcy property after the merger. The creditors of each member shall be fairly subject to the compensation in accordance with the legal order in the same procedure. In the case of reorganization through substantive consolidation, a unified classification of claims, adjustments to claims, and claims for compensation should be formulated in the draft of the reorganization plan.
37. Subsistence of the enterprise members after the substantive merger. If the bankruptcy liquidation is applied to the substantive merger rules, the members of the related companies shall be written off after the termination of the bankruptcy proceedings. When a substantial consolidation rule is applied for conciliation or reorganization, each affiliated enterprise shall be merged into one enterprise in principle. According to the settlement agreement or the reorganization plan, if there is a need to maintain the independence of individual companies, they should be dealt with separately in accordance with the relevant rules for the separation of enterprises.
38. Principles for the coordination of trial and jurisdiction of bankruptcy cases in related enterprises. If multiple related enterprise members have bankruptcy reasons but do not meet the conditions for substantive merger, the people's court may conduct coordination procedures for the multiple bankruptcy proceedings according to the application of the relevant entity, and may comprehensively consider factors such as the efficiency of the bankruptcy case hearing, the sequence of the bankruptcy filing, the size of the liabilities of the members, the place of residence of the core controlling company, etc., in accordance with the needs of program coordination, and then let the common superior court to determine a court to carry out centralized management.
39. Legal consequences of coordinating trials. Coordinating trials do not eliminate the creditor-debtor relationship among the members of the related company, and do not merge the property of the members of the related companies. The creditors of the members of the related companies still receive the legal compensation according to the property of the member of the enterprise. However, the creditor's right formed by the improper use of the associated relationship between the members of the related company shall be inferior to other common claims in the order of repayment, and the inferior creditor shall not be given priority for repayment of the specific property provided by other affiliated members.
VII. Linkage between execution procedures and bankruptcy proceedings
The effective link between execution procedures and bankruptcy procedures is a powerful step in advancing bankruptcy trials in an all-round way, and it is also an important measure to crack down on the “law enforcement difficulty”. The courts at all levels in the country must profoundly understand the significance of the execution of bankruptcy transfer work, and vigorously promote enforcement cases that meet bankruptcy conditions, including enforcement of cases that cannot be entered into bankruptcy proceedings and give full play to the institutional value of bankruptcy proceedings.
40. Execute the court's review of the notice, obligation to explain and transfer duties. The executive department must attach great importance to the connection between implementation and bankruptcy, and promote the transfer of eligible execution cases to bankruptcy procedures. If the enforcement court finds that the corporate entity as the executed person complies with the provisions of Article 2 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, it shall promptly inquire whether the parties agree to transfer the case to bankruptcy examination and explain the legal consequences. After the enforcement court makes a transfer decision, it shall notify all known enforcement courts with written notice and the enforcement court shall suspend the execution procedure for the executed person.
41. Transfer and receipt of cases transferred to bankruptcy. The enforcement courts and the transferred courts should strengthen coordination and cooperation in the transfer process to enhance the effectiveness of the work. When transferring the case, the enforcement court shall ensure that the material is complete, and the content and form conform to the provisions. The transferred court shall carefully review and give timely feedback, and shall not refuse to accept or postpone filing for no reason.
42. The removal of sealing measures or the transfer of sealed assets after the acceptance of bankruptcy cases. After the enforcement court receives the bankruptcy acceptance ruling, it shall relieve the measures for seizure, detainment and freezing of the debtor’s property; or issue a letter to transfer the disposal right of seizure, detainment and freezing of the property to the bankruptcy acceptance court, upon the request. The bankruptcy acceptance court may hold the enforcement court's letter of transfer and disposal to proceed with the seizure, detainment, freezing, relieve the seizure, detainment and freezing, or dispose of them.
If the enforcement court receives a bankruptcy acceptance ruling and refuses to relieve the measures of seizure, detainment or freezing, the bankruptcy acceptance court may request the superior court of the enforcement court to correct it according to law.
43. Sharing of information between the bankruptcy court and the executive branch. The bankruptcy acceptance court can use the execution and inspection control system to check the debtor’s property and improve the efficiency of the bankruptcy trial. The enforcement department should cooperate.
The local courts should establish the concept of synchronization of online and offline legal procedures, gradually implement online transfer of enforcement cases that meet the conditions for transfer, enhance the transparency of the transfer work, and improve the efficiency of related work such as case transfer, notification, delivery, and communication and coordination.
44. Strengthen the assessment and management of the transfer of bankruptcy work. Courts at all levels must combine the actual work to establish an assessment mechanism for the implementation of bankruptcy transfer work, scientifically set up assessment targets, and promote the implementation of bankruptcy transfers. Those who should have consulted the parties concerned without consulting, should have submitted for review without submitting, the transferred court violating the relevant regulations and refusing to accept bankruptcy transfer material for execution or filing, shall not only be included in the performance appraisal and performance appraisal system, but also be openly informed and traced responsibilities of related personnel seriously.
VIII. Construction of bankruptcy information
The meeting held that the national courts must further strengthen the informatization of bankruptcy trials, improve the transparency and credibility of bankruptcy cases, enhance the effectiveness of bankruptcy case trials, and promote the reorganization and regeneration of enterprises.
45. Give full play to the impetus of bankruptcy and reorganization case information platform to bankruptcy trial work. Courts at all levels shall, in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Supreme People's Court, regulate the examination of bankruptcy cases through the bankruptcy and reorganization case information platform, and be open entirely. It is necessary to further strengthen the information statistics and data retrieval functions of the information network, analyze and judge the bankruptcy cases of enterprises, find new situations in a timely manner, solve new problems, and improve the trial level of bankruptcy cases.
46. Constantly intensify the disclosure of information in bankruptcy and reorganization cases. It is necessary to increase the public content of the debtor’s corporate information, attract potential investors, promote the free flow and effective allocation of capital, technology, and management capabilities, and help the company reorganize and regenerate. It is necessary to ensure that creditors and other interested parties promptly and fully understand the progress of the case and the relevant financial affairs of the debtors, the draft of the reorganization plan, and the implementation of the reorganization plan, and maintain the right to know and the right to participate in proceedings of creditors and other interested parties.
47. Use information technology to improve the quality and efficiency of bankruptcy case processing. It is necessary to adapt to the development trend of informatization, actively guide the disposal of bankruptcy assets through online auctions, and improve the disposal benefits of bankruptcy assets. It is necessary to encourage and standardize the meeting of creditors through the Internet, improve efficiency, reduce bankruptcy expenses, and ensure that creditors and other entities participate in bankruptcy proceedings.
48. Give full play to the pivotal role of the people's court's bankruptcy and reorganization case information network. It is necessary to continuously improve and promote the use of bankruptcy and reorganization case information network, and to ensure that incremental data is entered into the information network in a timely manner. At the same time, the relevant inventory data should be filled in quickly to establish the pivotal position of the information network in corporate bankruptcy big data, and exert the promotion and exchange function of the information network, and expand the enthusiasm of all parties to use the information network.
IX. Cross-border bankruptcy
49. The principle of cross-border bankruptcy and reciprocity.When handling cross-border insolvency cases, the people's court must properly resolve the legal conflicts and contradictions in cross-border insolvency and reasonably determine the jurisdiction in cross-border insolvency cases. Under the principle of equal protection of similar claims, the balance between the interests of foreign creditors and the interests of creditors in China should be well-coordinated, and reasonable claims such as domestic workers’ claims and tax claims should be protected. Actively participate in and promote the negotiation and signing of international treaties on cross-border insolvency, explore new ways to apply the principle of reciprocity, strengthen the cooperation between courts and managers in cross-border insolvency, and promote the healthy and orderly development of international investment.
50. Protection of rights and balance of interests in cross-border bankruptcy cases. In accordance with the provisions of Article 5 of the Enterprise Bankruptcy Law, cross-border bankruptcy cooperation is carried out. After the people’s court has confirmed the judgment or ruling of the bankruptcy case made by the foreign court, the debtor’s property in the People’s Republic of China will remain after fully paying off the priority of the domestic security right holder, employee’s claims, social insurance fees, delinquent taxes, etc. The property may be allocated in accordance with the provisions of the foreign court.







2023年度法院工作报告






















